Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The normal activity of living carbon-containing matter is found to be about 15 decays per minute for every gram of carbon. This activity arises from the small proportion of radioactive `""_6^14"C"` present with the stable carbon isotope `""_6^12"C"`. When the organism is dead, its interaction with the atmosphere (which maintains the above equilibrium activity) ceases and its activity begins to drop. From the known half-life (5730 years) of `""_6^14"C"` and the measured activity, the age of the specimen can be approximately estimated. This is the principle of `""_6^14"C"` dating used in archaeology. Suppose a specimen from Mohenjodaro gives an activity of 9 decays per minute per gram of carbon. Estimate the approximate age of the Indus-Valley civilisation.
उत्तर
Decay rate of living carbon-containing matter, R = 15 decay/min
Let N be the number of radioactive atoms present in a normal carbon-containing matter.
Half-life of `""_6^14"C"`, `"T"_(1/2)` = 5730 years
The decay rate of the specimen obtained from the Mohenjodaro site:
R' = 9 decays/min
Let N' be the number of radioactive atoms present in the specimen during the Mohenjodaro period.
Therefore, we can relate the decay constant, λ and time, t as:
`"N"/"N'" = "R"/"R'" = "e"^(-lambda"t")`
`"e"^(-lambda"t") = 9/15 = 3/5`
`-lambda"t" = log_"e" 3/5 = -0.5108`
∴ `"t" = 0.5108/lambda`
But `lambda = 0.639/"T"_"1/2" = 0.693/5730`
∴ t = `0.5108/(0.693/5730)`
= 4223.5 years
Hence, the approximate age of the Indus-Valley civilisation is 4223.5 years.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is it found experimentally difficult to detect neutrinos in nuclear β-decay?
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
Obtain the amount of `""_27^60"Co"` necessary to provide a radioactive source of 8.0 mCi strength. The half-life of `""_27^60"Co"` is 5.3 years.
The radionuclide 11C decays according to
\[\ce{^11_6C -> ^11_5B + e+ + \text{v}}\] : T1/2 = 20.3 min
The maximum energy of the emitted positron is 0.960 MeV.
Given the mass values: `"m"(""_6^11"C") = 11.011434 u and "m"(""_6^11"B") = 11.009305 "u"`
Calculate Q and compare it with the maximum energy of the positron emitted.
Define 'activity' of a radioactive substance ?
In a given sample, two radioisotopes, A and B, are initially present in the ration of 1 : 4. The half lives of A and B are respectively 100 years and 50 years. Find the time after which the amounts of A and B become equal.
A radioactive isotope is being produced at a constant rate dN/dt = R in an experiment. The isotope has a half-life t1/2. Show that after a time t >> t1/2 the number of active nuclei will become constant. Find the value of this constant.
Obtain a relation between the half-life of a radioactive substance and decay constant (λ).
Disintegration rate of a sample is 1010 per hour at 20 hours from the start. It reduces to 6.3 x 109 per hour after 30 hours. Calculate its half-life and the initial number of radioactive atoms in the sample.
Which one of the following nuclei has shorter meant life?
The half-life of a radioactive sample undergoing `alpha` - decay is 1.4 x 1017 s. If the number of nuclei in the sample is 2.0 x 1021, the activity of the sample is nearly ____________.
After 1 hour, `(1/8)^"th"` of the initial mass of a certain radioactive isotope remains undecayed. The half-life of the isotopes is ______.
Two radioactive materials Y1 and Y2 have decay constants '5`lambda`' and `lambda` respectively. Initially they have same number of nuclei. After time 't', the ratio of number of nuclei of Y1 to that of Y2 is `1/"e"`, then 't' is equal to ______.
Two electrons are ejected in opposite directions from radioactive atoms in a sample of radioactive material. Let c denote the speed of light. Each electron has a speed of 0.67 c as measured by an observer in the laboratory. Their relative velocity is given by ______.
If 10% of a radioactive material decay in 5 days, then the amount of original material left after 20 days is approximately :
Draw a graph showing the variation of decay rate with number of active nuclei.
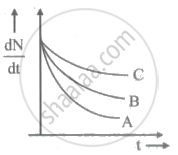
Which sample, A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?
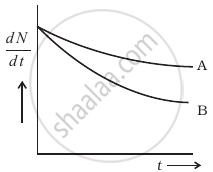
Consider a radioactive nucleus A which decays to a stable nucleus C through the following sequence:
A→B→C
Here B is an intermediate nuclei which is also radioactive. Considering that there are N0 atoms of A initially, plot the graph showing the variation of number of atoms of A and B versus time.
The radioactivity of an old sample of whisky due to tritium (half-life 12.5 years) was found to be only about 4% of that measured in a recently purchased bottle marked 10 years old. The age of a sample is ______ years.
The half-life of `""_82^210Pb` is 22.3 y. How long will it take for its activity 0 30% of the initial activity?
