Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of 10 years. How long will it take for the activity to reduce to 3.125% ?
उत्तर १
Half-life of the radioactive isotope = T years
Original amount of the radioactive isotope = N0
a) After decay, the amount of the radioactive isotope = N
It is given that only 3.125% of N0 remains after decay. Hence, we can write
`"N"/"N"_0` = 3.125% = `3.125/100 = 1/32`
But `"N"/"N"_0 = "e"^(-lambda"t")`
Where,
λ = Decay constant
t = Time
∴ `-lambda"t" = 1/32`
`-lambda"t" =ln 1 - ln32`
`-lambda"t" = 0 - 3.4657`
`"t" = 3.4657/lambda`
Since `lambda = 0.693/"T"`
∴ `"t" = 3.466/(0.693/"T") ≈ 5"T years"`
Hence, the isotope will take about 5T years to reduce to 3.125% of its original value.
b) After decay, the amount of the radioactive isotope = N
It is given that only 1% of N0 remains after decay. Hence, we can write:
`"N"/"N"_0` = 1% = `1/100`
But `"N"/"N"_0 = "e"^(-lambda"t")`
∴ `"e"^(-lambda"t") = 1/100`
`-lambda"t" = ln 1 - ln 100`
`"t" = 4.6052/lambda`
Since `lambda = 0.693/"T"`
∴ `t = 4.6052/(0.693/"T") = 6.645 "T years"`
Hence, the isotope will take about 6.645T years to reduce to 1% of its original value.
उत्तर २
`A_0 = 100`
`A_1 = 3.125`
`A_t = A_0.e^(-lambdat)`
`3.125 = 100e^(-0.693/10) t`
`3.125/100 = e^(-0.0693 t)`
`100/3.125 = e^(0.0693t)`
`log_e 100/3.125 = 0.0693t`
`t_2 = (2.303log_10^32)/0.0693`
t = 50.1 year
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The decay constant of radioactive substance is 4.33 x 10-4 per year. Calculate its half life period.
How is the mean life of a given radioactive nucleus related to the decay constant?
Obtain the amount of `""_27^60"Co"` necessary to provide a radioactive source of 8.0 mCi strength. The half-life of `""_27^60"Co"` is 5.3 years.
The Q value of a nuclear reaction A + b → C + d is defined by
Q = [mA+ mb − mC − md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^12_6C + ^12_6C ->^20_10Ne + ^4_2He}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12C)` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
Define the activity of a given radioactive substance. Write its S.I. unit.
A radioactive nucleus ‘A’ undergoes a series of decays according to the following scheme:
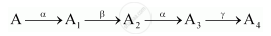
The mass number and atomic number of A are 180 and 72 respectively. What are these numbers for A4?
A freshly prepared radioactive source of half-life 2 h emits radiation of intensity which is 64 times the permissible safe level. The minimum time after which it would be possible to work safely with this source is
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the beta particle emitted in the following decay scheme:
12N → 12C* + e+ + v
12C* → 12C + γ (4.43MeV).
The atomic mass of 12N is 12.018613 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
Obtain a relation between the half-life of a radioactive substance and decay constant (λ).
What is the amount of \[\ce{_27^60Co}\] necessary to provide a radioactive source of strength 10.0 mCi, its half-life being 5.3 years?
A radioactive element disintegrates for an interval of time equal to its mean lifetime. The fraction that has disintegrated is ______
The half-life of a radioactive sample undergoing `alpha` - decay is 1.4 x 1017 s. If the number of nuclei in the sample is 2.0 x 1021, the activity of the sample is nearly ____________.
After 1 hour, `(1/8)^"th"` of the initial mass of a certain radioactive isotope remains undecayed. The half-life of the isotopes is ______.
Two electrons are ejected in opposite directions from radioactive atoms in a sample of radioactive material. Let c denote the speed of light. Each electron has a speed of 0.67 c as measured by an observer in the laboratory. Their relative velocity is given by ______.
The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 20 hrs. The fraction of the original activity that will remain after 40 hrs is ______.
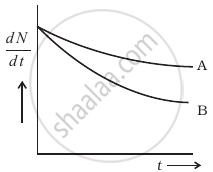
Which sample, A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?
The radioactivity of an old sample of whisky due to tritium (half-life 12.5 years) was found to be only about 4% of that measured in a recently purchased bottle marked 10 years old. The age of a sample is ______ years.
The half-life of `""_82^210Pb` is 22.3 y. How long will it take for its activity 0 30% of the initial activity?
