Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The stability order for carbocation is _______.
(A) 2° > 3° > 1°
(B) 3° > 2° > 1°
(C) 3° > 1° > 2°
(D) 1° > 3° > 2°
उत्तर
(B) 3° > 2° > 1°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the main products when methyl chloride is treated with AgCN.
What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Toluene to benzyl alcohol
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis?
Given reasons: SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
Which would undergo SN2 reaction faster in the following pair and why ?
CH3 – CH2 – Br and CH3 – CH2 – I
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide
alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide.
AgCN reacts with haloalkanes to form isocyanide. Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanides as the main product. Why?
In the reaction, \[\ce{R - X + NaOR' -> ROR’ + X}\] ( – ve ion). The main product formed is:
Which one is most reactive towards SN1 reaction?
Which one of the following halogen compounds is difficult to be hydrolysed by SN1 mechanism?
Most reactive halide towards SN1 reaction is ____________.
SN2 mechanism proceeds through intervention of ____________.
Isopropyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis by:
Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by SN2 mechanism because of ____________.
SN1 reaction of alkyl halides lead to ___________.
The correct order of increasing the reactivity of C–X bond towards nucleophile in following compounds.
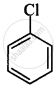
(I)
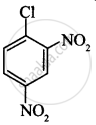
(II)
(CH3)3CCl
(III)
(CH3)2CHCl
(IV)
Which of the following compound will undergo racemisation when reacts with aq. KOH?
(i)
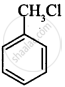
(ii)
CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3-CH-CH2Cl}
\end{array}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\ce{CH3-C-Cl}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{C2H5}
\end{array}\]
Complete the following analogy:
Same molecular formula but different structures: A : : Non superimposable mirror images: B
Which reagent will you use for the following reaction?
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH3 -> CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl + CH3CH2CHClCH3}\]
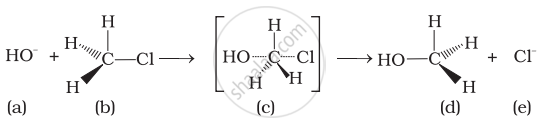
Which of the statements are correct about above reaction?
(i) (a) and (e) both are nucleophiles.
(ii) In (c) carbon atom is sp3 hybridised.
(iii) In (c) carbon atom is sp2 hybridised.
(iv) (a) and (e) both are electrophiles.
How do polar solvents help in the first step in SN1 mechanism?
When CH3CH2CHCl2 is treated NaNH2 product formed is:-
In SN1 reactions, the correct order of reactivity for the following compounds:
CH3Cl, CH3CH2Cl, (CH3)2CHCl and (CH3)3CCl is ______.
Racemisation occurs in ______.
Assertion (A) : Nucleophilic substitution of iodoethane is easier than chloroethane.
Reason (R) : Bond enthalpy of C-I bond is less than that of C-Cl bond.
Convert bromoethane to propanamine.
Explain why Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CHCH2CH2Br}\\|\phantom{.........}\\\ce{CH3}\phantom{......}\end{array}\] or \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3CH2CHCH2Br}\\\phantom{}|\\\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\end{array}\]
