Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The time constant of an LR circuit is 40 ms. The circuit is connected at t = 0 and the steady-state current is found to be 2.0 A. Find the current at (a) t = 10 ms (b) t = 20 ms, (c) t = 100 ms and (d) t = 1 s.
उत्तर
Given:-
Time constant of the given LR circuit, τ = 40 ms
Steady-state current in the circuit, i0 = 2 A
(a) Current at time t = 10 ms:
i = i0(1 − e−t/τ)
= 2(1 − e−10/40)
= 2(1 − e−1/4)
= 2(1 − 0.7788)
= 0.4422 A
= 0.44 A
(b) Current at time t = 20 ms:
i = i0(1 − e−t/τ)
= 2(1 − e−20/40)
= 2(1 − e−1/2)
= 2(1 − 0.606)
= 0.788 A
= 0.79 A
(c) Current at t = 100 ms:
i = i0(1 − e−t/τ)
= 2(1 − e−100/40)
= 2(1 − e−10/4)
= 2(1 − e−5/2)
= 2(1−0.082)
=1.835 A
= 1.8 A
(d) Current at t = 1 s:
i = i0(1 − e−t/τ)
= 2(1 − e−1000/40)
= 2(1 − e−100/4)
= 2(1 − e−25)
= 2 × 1 A
= 2 A
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A series LCR circuit is connected to a source having voltage v = vm sin ωt. Derive the expression for the instantaneous current I and its phase relationship to the applied voltage.
Obtain the condition for resonance to occur. Define ‘power factor’. State the conditions under which it is (i) maximum and (ii) minimum.
A coil of resistance 40 Ω is connected across a 4.0 V battery. 0.10 s after the battery is connected, the current in the coil is 63 mA. Find the inductance of the coil.
An inductor-coil of inductance 17 mH is constructed from a copper wire of length 100 m and cross-sectional area 1 mm2. Calculate the time constant of the circuit if this inductor is joined across an ideal battery. The resistivity of copper = 1.7 × 10−8 Ω-m.
The current in a discharging LR circuit without the battery drops from 2.0 A to 1.0 A in 0.10 s. (a) Find the time constant of the circuit. (b) If the inductance of the circuit 4.0 H, what is its resistance?
Consider the circuit shown in figure. (a) Find the current through the battery a long time after the switch S is closed. (b) Suppose the switch is again opened at t = 0. What is the time constant of the discharging circuit? (c) Find the current through the inductor after one time constant.
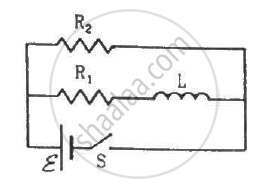
What will be the potential difference in the circuit when direct current is passed through the circuit?
A series LCR circuit with R = 20 Ω, L = 1.5 H and C = 35 µF is connected to a variable-frequency 200 V ac supply. When the frequency of the supply equals the natural frequency of the circuit, what is the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle?
Keeping the source frequency equal to the resonating frequency of the series LCR circuit, if the three elements, L, C and R are arranged in parallel, show that the total current in the parallel LCR circuit is minimum at this frequency. Obtain the current rms value in each branch of the circuit for the elements and source specified for this frequency.
For a series LCR-circuit, the power loss at resonance is ______.
In series combination of R, L and C with an A.C. source at resonance, if R = 20 ohm, then impedence Z of the combination is ______.
In an LCR series a.c. circuit, the voltage across each of the components, L, C and R is 50V. The voltage across the LC combination will be ______.
A coil of 40 henry inductance is connected in series with a resistance of 8 ohm and the combination is joined to the terminals of a 2 volt battery. The time constant of the circuit is ______.
In series LCR circuit, the phase angle between supply voltage and current is ______.
A series LCR circuit contains inductance 5 mH, capacitance 2µF and resistance ion. If a frequency A.C. source is varied, what is the frequency at which maximum power is dissipated?
If the rms current in a 50 Hz ac circuit is 5 A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is ______.
To reduce the resonant frequency in an LCR series circuit with a generator ______.
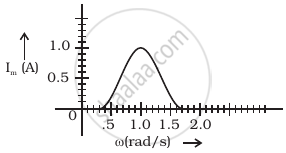
In series LCR circuit, the plot of Imax vs ω is shown in figure. Find the bandwidth and mark in the figure.