Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What will be the potential difference in the circuit when direct current is passed through the circuit?
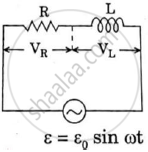
उत्तर
In case of DC ω = 0
XL = ωL = 0 Ω R = 160 Ω
Z = 160 Ω
e = 160 × i
e = 160V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a series LCR circuit, obtain the condition under which watt-less current flows in the circuit ?
Show that in an a.c. circuit containing a pure inductor, the voltage is ahead of current by π/2 in phase ?
A coil of resistance 40 Ω is connected across a 4.0 V battery. 0.10 s after the battery is connected, the current in the coil is 63 mA. Find the inductance of the coil.
The time constant of an LR circuit is 40 ms. The circuit is connected at t = 0 and the steady-state current is found to be 2.0 A. Find the current at (a) t = 10 ms (b) t = 20 ms, (c) t = 100 ms and (d) t = 1 s.
A constant current exists in an inductor-coil connected to a battery. The coil is short-circuited and the battery is removed. Show that the charge flown through the coil after the short-circuiting is the same as that which flows in one time constant before the short-circuiting.
In series LCR circuit, the phase angle between supply voltage and current is ______.
At resonant frequency the current amplitude in series LCR circuit is ______.
The phase diffn b/w the current and voltage at resonance is
A series LCR circuit containing a resistance of 120 Ω has angular resonance frequency 4 × 105 rad s-1. At resonance the voltage across resistance and inductance are 60 V and 40 V respectively. At what frequency the current in the circuit lags the voltage by 45°. Give answer in ______ × 105 rad s-1.
When an alternating voltage of 220V is applied across device X, a current of 0.25A flows which lags behind the applied voltage in phase by π/2 radian. If the same voltage is applied across another device Y, the same current flows but now it is in phase with the applied voltage.
- Name the devices X and Y.
- Calculate the current flowing in the circuit when the same voltage is applied across the series combination of X and Y.
