Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What will be the potential difference in the circuit when direct current is passed through the circuit?
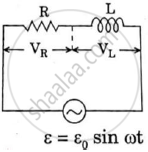
उत्तर
In case of DC ω = 0
XL = ωL = 0 Ω R = 160 Ω
Z = 160 Ω
e = 160 × i
e = 160V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A source of ac voltage v = v0 sin ωt, is connected across a pure inductor of inductance L. Derive the expressions for the instantaneous current in the circuit. Show that average power dissipated in the circuit is zero.
A solenoid having inductance 4.0 H and resistance 10 Ω is connected to a 4.0 V battery at t = 0. Find (a) the time constant, (b) the time elapsed before the current reaches 0.63 of its steady-state value, (c) the power delivered by the battery at this instant and (d) the power dissipated in Joule heating at this instant.
The magnetic field at a point inside a 2.0 mH inductor-coil becomes 0.80 of its maximum value in 20 µs when the inductor is joined to a battery. Find the resistance of the circuit.
The current in a discharging LR circuit without the battery drops from 2.0 A to 1.0 A in 0.10 s. (a) Find the time constant of the circuit. (b) If the inductance of the circuit 4.0 H, what is its resistance?
An ac circuit as shown in the figure has an inductor of inductance L and a resistor or resistance R connected in series. Using the phasor diagram, explain why the voltage in the circuit will lead the current in phase.
Choose the correct answer from given options
The phase difference between the current and the voltage in series LCR circuit at resonance is
A series LCR circuit with R = 20 Ω, L = 1.5 H and C = 35 µF is connected to a variable-frequency 200 V ac supply. When the frequency of the supply equals the natural frequency of the circuit, what is the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle?
Figure shows a series LCR circuit connected to a variable frequency 230 V source. L = 5.0 H, C = 80 µF, R = 40 Ω.
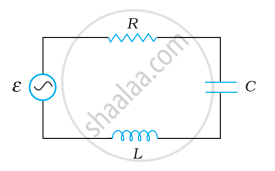
- Determine the source frequency which drives the circuit in resonance.
- Obtain the impedance of the circuit and the amplitude of current at the resonating frequency.
- Determine the rms potential drops across the three elements of the circuit. Show that the potential drop across the LC combination is zero at the resonating frequency.
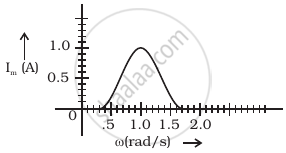
In series LCR circuit, the plot of Imax vs ω is shown in figure. Find the bandwidth and mark in the figure.
An alternating voltage of 220 V is applied across a device X. A current of 0.22 A flows in the circuit and it lags behind the applied voltage in phase by π/2 radian. When the same voltage is applied across another device Y, the current in the circuit remains the same and it is in phase with the applied voltage.
- Name the devices X and Y and,
- Calculate the current flowing in the circuit when the same voltage is applied across the series combination of X and Y.
