Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An inductor-coil of inductance 17 mH is constructed from a copper wire of length 100 m and cross-sectional area 1 mm2. Calculate the time constant of the circuit if this inductor is joined across an ideal battery. The resistivity of copper = 1.7 × 10−8 Ω-m.
उत्तर
Given:-
Inductance, L = 17 mH
Length of the wire, l = 100 m
Cross-sectional area of the wire, A = 1 mm2 = 1 × 10−6 m2
Resistivity of copper, ρ = 1.7 × 10−8 Ω-m
Now,
\[R = \frac{\rho l}{A}\]
\[ = \frac{1 . 7 \times {10}^{- 8} \times 100}{1 \times {10}^{- 6}} = 1 . 7 \Omega\]
The time constant of the L-R circuit is given by
\[\tau = \frac{L}{R} = \frac{17 \times {10}^{- 3}}{1 . 7}\]
\[= {10}^{- 2} s = 10 ms\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a series LCR circuit, obtain the condition under which watt-less current flows in the circuit ?
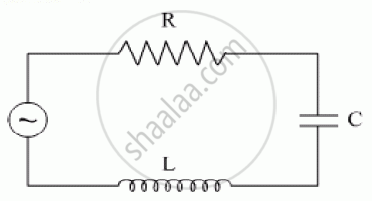
The figure shows a series LCR circuit with L = 10.0 H, C = 40 μF, R = 60 Ω connected to a variable frequency 240 V source, calculate
(i) the angular frequency of the source which drives the circuit at resonance,
(ii) the current at the resonating frequency,
(iii) the rms potential drop across the inductor at resonance.
The magnetic field at a point inside a 2.0 mH inductor-coil becomes 0.80 of its maximum value in 20 µs when the inductor is joined to a battery. Find the resistance of the circuit.
A constant current exists in an inductor-coil connected to a battery. The coil is short-circuited and the battery is removed. Show that the charge flown through the coil after the short-circuiting is the same as that which flows in one time constant before the short-circuiting.
(i) An a.c. source of emf ε = 200 sin omegat is connected to a resistor of 50 Ω . calculate :
(1) Average current (`"I"_("avg")`)
(2) Root mean square (rms) value of emf
(ii) State any two characteristics of resonance in an LCR series circuit.
Answer the following question.
What is the phase difference between the voltages across the inductor and the capacitor at resonance in the LCR circuit?
Answer the following question.
Draw the diagram of a device that is used to decrease high ac voltage into a low ac voltage and state its working principle. Write four sources of energy loss in this device.
Derive an expression for the average power dissipated in a series LCR circuit.
A series LCR circuit with L = 0.12 H, C = 480 nF, R = 23 Ω is connected to a 230 V variable frequency supply.
(a) What is the source frequency for which current amplitude is maximum. Obtain this maximum value.
(b) What is the source frequency for which average power absorbed by the circuit is maximum. Obtain the value of this maximum power.
(c) For which frequencies of the source is the power transferred to the circuit half the power at resonant frequency? What is the current amplitude at these frequencies?
(d) What is the Q-factor of the given circuit?
In a series LCR circuit supplied with AC, ______.
If an LCR series circuit is connected to an ac source, then at resonance the voltage across ______.
A coil of 40 henry inductance is connected in series with a resistance of 8 ohm and the combination is joined to the terminals of a 2 volt battery. The time constant of the circuit is ______.
In series LCR circuit, the phase angle between supply voltage and current is ______.
At resonant frequency the current amplitude in series LCR circuit is ______.
A series LCR circuit containing 5.0 H inductor, 80 µF capacitor and 40 Ω resistor is connected to 230 V variable frequency ac source. The angular frequencies of the source at which power transferred to the circuit is half the power at the resonant angular frequency are likely to be ______.
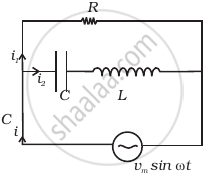
Consider the LCR circuit shown in figure. Find the net current i and the phase of i. Show that i = v/Z`. Find the impedance Z for this circuit.
A series LCR circuit is connected to an ac source. Using the phasor diagram, derive the expression for the impedance of the circuit.
Draw a labelled graph showing variation of impedance (Z) of a series LCR circuit Vs frequency (f) of the ac supply. Mark the resonant frequency as f0·
