Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and 1.0 × 10−6 C are placed at a separation of 10 cm. Where should a third charge be placed, such that it experiences no net force due to these charges?
उत्तर
Given:
\[q_1 = 2 . 0 \times {10}^{- 6} C\]
\[ q_2 = 1 . 0 \times {10}^{- 6} C\]
Let the third charge, q, be placed at a distance of x cm from charge q1, as shown in the figure.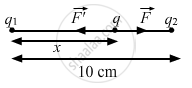
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times 2 \times {10}^{- 6} \times q}{x^2} = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times {10}^{- 6} \times q}{\left( 10 - x \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x^2 = 2 \left( 10 - x \right)^2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow x^2 - 40x + 200 = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 20 \pm 10\sqrt{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 5 . 9 \text{ cm } ( \because x \neq 20 + 10\sqrt{2})\]
So, the third charge should be placed at a distance of 5.9 cm from q1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
- Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centers separated by a distance of 50 cm. What is the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion if the charge on each is 6.5 × 10−7 C? The radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation.
- What is the force of repulsion if each sphere is charged double the above amount, and the distance between them is halved?
Three-point charges q, – 4q and 2q are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side 'l' as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the magnitude of the resultant electric force acting on the charge q

(b) Find out the amount of the work done to separate the charges at infinite distance.
Four charges +q, −q, +q and −q are to be arranged respectively at the four corners of a square ABCD of side 'a'.
(a) Find the work required to put together this arrangement.
(b) A charge q0 is brought to the centre of the square, the four charges being held fixed. How much extra work is needed to do this ?
Write any two important points of similarities and differences each between Coulomb's law for the electrostatic field and Biot-Savart's law of the magnetic field ?
Does the force on a charge due to another charge depend on the charges present nearby?
A charge of 1.0 C is placed at the top of your college building and another equal charge at the top of your house. Take the separation between the two charges to be 2.0 km. Find the force exerted by the charges on each other. How many times your weight is this force?
Suppose an attractive nuclear force acts between two protons which may be written as F=Ce−kr/r2. Write down the dimensional formulae and appropriate SI units of C and k.
Three equal charges, 2.0 × 10−6 C each, are held at the three corners of an equilateral triangle of side 5 cm. Find the Coulomb force experienced by one of the charges due to the other two.
Find the speed of the electron in the ground state of a hydrogen atom. The description of ground state is given in the previous problem.
A particle with a charge of 2.0 × 10−4 C is placed directly below and at a separation of 10 cm from the bob of a simple pendulum at rest. The mass of the bob is 100 g. What charge should the bob be given so that the string becomes loose?
Two identically-charged particles are fastened to the two ends of a spring of spring constant 100 N m−1 and natural length 10 cm. The system rests on a smooth horizontal table. If the charge on each particle is 2.0 × 10−8 C, find the extension in the length of the spring. Assume that the extension is small as compared to the natural length. Justify this assumption after you solve the problem.
Two particles A and B, each carrying a charge Q, are held fixed with a separation dbetween them. A particle C of mass m and charge q is kept at the middle point of the line AB. If it is displaced through a distance x perpendicular to AB, what would be the electric force experienced by it?
Two particles A and B, each carrying a charge Q, are held fixed with a separation dbetween them. A particle C of mass m and charge q is kept at the middle point of the line AB. Under what conditions will the particle C execute simple harmonic motion if it is released after such a small displacement? Find the time period of the oscillations if these conditions are satisfied.
Two particles A and B possessing charges of +2.00 × 10−6 C and of −4.00 × 10−6 C, respectively, are held fixed at a separation of 20.0 cm. Locate the points (s) on the line AB, where (a) the electric field is zero (b) the electric potential is zero.
Two particles of masses 5.0 g each and opposite charges of +4.0 × 10−5 C and −4.0 × 10−5 C are released from rest with a separation of 1.0 m between them. Find the speeds of the particles when the separation is reduced to 50 cm.
Answer the following question.
What is relative permittivity?
Solve numerical example.
Three equal charges of 10×10-8 C respectively, each located at the corners of a right triangle whose sides are 15 cm, 20 cm, and 25cm respectively. Find the force exerted on the charge located at the 90° angle.
Two point charges +3 µC and +8 µC repel each other with a force of 40 N. If a charge of -5 µC is added to each of them, then force between them will become ______.
Which of the following statements about nuclear forces is not true?
