Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two equal charges, 2.0 × 10−7 C each, are held fixed at a separation of 20 cm. A third charge of equal magnitude is placed midway between the two charges. It is now moved to a point 20 cm from both the charges. How much work is done by the electric field during the process?
उत्तर
Let the third charge be moved from point A to point B.
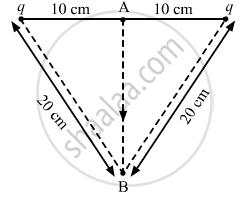
Magnitude of the charges, q = 2.0 × 10−7 C
Distance of both the charges from point A, r = 10 cm =0.1 m
Distance of both the charges from point B, r' = 20 cm =0.2 m
Potential at A,
\[V_A = 2 \times \frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{q}{r}\]
Potential at B,
\[V_B = 2 \times \frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{q}{r'}\]
Work done,
\[\Rightarrow W = 2 \times {10}^{- 7} \left[ \frac{2 \times 2 \times {10}^{- 7}}{4 \pi\epsilon_0}\left( \frac{1}{0 . 1} - \frac{1}{0 . 2} \right) \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = 3 . 6 \times {10}^{- 3}\] J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Four point charges qA = 2 μC, qB = −5 μC, qC = 2 μC, and qD = −5 μC are located at the corners of a square ABCD of side 10 cm. What is the force on a charge of 1 μC placed at the centre of the square?
Two charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and 1.0 × 10−6 C are placed at a separation of 10 cm. Where should a third charge be placed, such that it experiences no net force due to these charges?
NaCl molecule is bound due to the electric force between the sodium and the chlorine ions when one electron of sodium is transferred to chlorine. Taking the separation between the ions to be 2.75 × 10−8 cm, find the force of attraction between them. State the assumptions (if any) that you have made.
Find the speed of the electron in the ground state of a hydrogen atom. The description of ground state is given in the previous problem.
Ten positively-charged particles are kept fixed on the x-axis at points x = 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, ...., 100 cm. the first particle has a charge 1.0 × 10−8 C, the second 8 × 10−8 C, the third 27 × 10−8 C and so on. The tenth particle has a charge 1000 × 10−8 C. Find the magnitude of the electric force acting on a 1 C charge placed at the origin.
Two identical pith balls, each carrying a charge q, are suspended from a common point by two strings of equal length l. Find the mass of each ball if the angle between the strings is 2θ in equilibrium.
A particle with a charge of 2.0 × 10−4 C is placed directly below and at a separation of 10 cm from the bob of a simple pendulum at rest. The mass of the bob is 100 g. What charge should the bob be given so that the string becomes loose?
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C is held fixed on a horizontal table. A second charged particle of mass 80 g stays in equilibrium on the table at a distance of 10 cm from the first charge. The coefficient of friction between the table and this second particle is μ = 0.2. Find the range within which the charge of this second particle may lie.
A point charge produces an electric field of magnitude 5.0 NC−1 at a distance of 40 cm from it. What is the magnitude of the charge?
How much work has to be done in assembling three charged particles at the vertices of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure?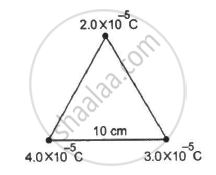
Solve numerical example.
Three equal charges of 10×10-8 C respectively, each located at the corners of a right triangle whose sides are 15 cm, 20 cm, and 25cm respectively. Find the force exerted on the charge located at the 90° angle.
A total charge Q is broken in two parts Q1 and Q2 and they are placed at a distance R from each other. The maximum force of repulsion between them will occur, when ____________.
Two identical thin rings, each of radius a meter, are coaxially placed at a distance R meter apart. If Q1 coulomb and Q2 coulomb are respectively the charges uniformly spread on the two rings, the work done in moving a charge q coulomb from the centre of one ring to that of the other is ______.
Two charges of equal magnitudes kept at a distance r exert a force F on each other. If the charges are halved and distance between them is doubled, then the new force acting on each charge is ______.
The S.I unit of electric permittivity is
Which of the following statements about nuclear forces is not true?
Four charges equal to −Q are placed at the four a corners of a square and charge q is at its centre. If the system is in equilibrium, the value of q is ______.
What is meant by the statement: "Relative permittivity of water is 81"?
