Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two parallel wires separated by a distance of 10 cm carry currents of 10 A and 40 A along the same direction. Where should a third current by placed so that it experiences no magnetic force?
उत्तर
Let the third wire W3 having current i in upward direction be placed x cm from the 10 A current wire.

The magnetic force per unit length on a wire due to a parallel current-carrying wire is given by
\[ \Rightarrow 10 - x = 4x\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2 cm\]
Thus, wire W3 is placed 2 cm from the 10 A current wire.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two infinitely long straight parallel wires, '1' and '2', carrying steady currents I1 and I2 in the same direction are separated by a distance d. Obtain the expression for the magnetic field `vecB`due to the wire '1' acting on wire '2'. Hence find out, with the help of a suitable diagram, the magnitude and direction of this force per unit length on wire '2' due to wire '1'. How does the nature of this force changes if the currents are in opposite direction? Use this expression to define the S.I. unit of current.
Using the concept of force between two infinitely long parallel current carrying conductors, define one ampere of current.
Two long straight parallel conductors 'a' and 'b', carrying steady currents Ia and Ib are separated by a distance d. Write the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field produced by the conductor 'a' at the points along the conductor 'b'. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, what is the nature and magnitude of the force between the two conductors?
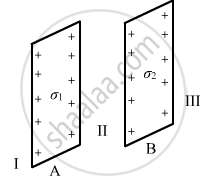
Two infinitely large plane thin parallel sheets having surface charge densities σ1 and σ2 (σ1 > σ2) are shown in the figure. Write the magnitudes and directions of the net fields in the regions marked II and III.
Derive the expression for force per unit length between two long straight parallel current carrying conductors. Hence define one ampere.
and ```vecE` and `vecB`denote electric and magnetic fields in a frame S and `vecE`→ and `vecB` in another frame S' moving with respect to S at a velocity `vecV` Two of the following equations are wrong. Identify them.
(a) `B_y^, = B_y + (vE_z)/c^2`
(b) `E_y^' = E_y - (vB_z)/(c^2)`
`(c) Ey = By + vE_z`
`(d) E_y = E_y + vB_z`
A long, straight wire carries a current along the z-axis, One can find two points in the x−y plane such that
(a) the magnetic fields are equal
(b) the directions of the magnetic fields are the same
(c) the magnitudes of the magnetic fields are equal
(d) the field at one point is opposite to that at the other point.
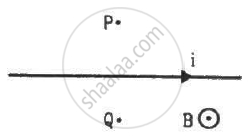
A long, straight wire carrying a current of 1.0 A is placed horizontally in a uniform magnetic field B = 1.0 × 10−5 T pointing vertically upward figure. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at the points P and Q, both situated at a distance of 2.0 cm from the wire in the same horizontal plane.
A straight wire of length l can slide on two parallel plastic rails kept in a horizontal plane with a separation d. The coefficient of friction between the wire and the rails is µ. If the wire carries a current i, what minimum magnetic field should exist in the space in order to slide the wire on the rails?
A rectangular coil of 100 turns has length 5 cm and width 4 cm. It is placed with its plane parallel to a uniform magnetic field and a current of 2 A is sent through the coil. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B if the torque acting on the coil is 0.2 N m−1
Two parallel wires carry equal currents of 10 A along the same direction and are separated by a distance of 2.0 cm. Find the magnetic field at a point which is 2.0 cm away from each of these wires.
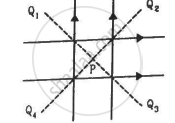
Four long, straight wires, each carrying a current of 5.0 A, are placed in a plane as shown in figure. The points of intersection form a square of side 5.0 cm.
(a) Find the magnetic field at the centre P of the square.
(b) Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4, are points situated on the diagonals of the square and at a distance from P that is equal to the diagonal of the square. Find the magnetic fields at these points.
Consider a 10-cm long piece of a wire which carries a current of 10 A. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field due to the piece at a point which makes an equilateral triangle with the ends of the piece.
A straight, how wire carries a current of 20 A. Another wire carrying equal current is placed parallel to it. If the force acting on a length of 10 cm of the second wire is 2.0 × 10−5 N, what is the separation between them?
Define Ampere in terms of force between two current carrying conductors.
The nature of parallel and anti-parallel currents are ______.
Two long straight parallel current-carrying conductors are kept ‘a’ distant apart in the air. The direction of current in both the conductors is the same. Find the magnitude of force per unit length and the direction of the force between them. Hence define one ampere.
