Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using the definition, prove that the function f: A→ B is invertible if and only if f is both one-one and onto
उत्तर
Let f: A → B be many-one function.
Let f(a) = p and f(b) = p
So, for inverse function we will have f-1(p) = a and f-1(p) = b
Thus, in this case inverse function is not defined as we have two images ‘a and b’ for one pre-image ‘p’.
But for f to be invertible it must be one-one.
Now, let f: A → B is not onto function.
Let B = {p, q, r} and range of f be {p, q}.
Here image ‘r’ has not any pre-image, which will have no image in set A.
And for f to be invertible it must be onto.
Thus, ‘f’ is invertible if and only if ‘f’ is both one-one and onto.
A function f = X → Y is invertible iff f is a bijective function.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the function f: R* → R* defined by `f(x) = 1/x` is one-one and onto, where R* is the set of all non-zero real numbers. Is the result true if the domain R* is replaced by N, with co-domain being same as R?
Check the injectivity and surjectivity of the following function:
f: R → R given by f(x) = x2
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. Show that f is one-one.
Show that the function f: R → R given by f(x) = x3 is injective.
Let f: R → R be the Signum Function defined as
f(x) = `{(1,x>0), (0, x =0),(-1, x< 0):}`
and g: R → R be the Greatest Integer Function given by g(x) = [x], where [x] is greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then does fog and gof coincide in (0, 1]?
If the function `f(x) = sqrt(2x - 3)` is invertible then find its inverse. Hence prove that `(fof^(-1))(x) = x`
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection : f : Z → Z given by f(x) = x2
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = |x|
Classify the following function as injection, surjection or bijection :
f : R → R, defined by f(x) = x3 + 1
Find gof and fog when f : R → R and g : R → R is defined by f(x) = 2x + 3 and g(x) = x2 + 5 .
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be defined by f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x + 1. Show that fog ≠ gof.
Find fog and gof if : f(x) = sin−1 x, g(x) = x2
Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4}; B = {3, 5, 7, 9}; C = {7, 23, 47, 79} and f : A → B, g : B → C be defined as f(x) = 2x + 1 and g(x) = x2 − 2. Express (gof)−1 and f−1 og−1 as the sets of ordered pairs and verify that (gof)−1 = f−1 og−1.
Consider f : R → R given by f(x) = 4x + 3. Show that f is invertible. Find the inverse of f.
If f : R → (−1, 1) defined by `f (x) = (10^x- 10^-x)/(10^x + 10 ^-x)` is invertible, find f−1.
If f : C → C is defined by f(x) = x4, write f−1 (1).
Let \[f : \left( - \frac{\pi}{2}, \frac{\pi}{2} \right) \to R\] be a function defined by f(x) = cos [x]. Write range (f).
Let A = {1, 2, 3}, B = {4, 5, 6, 7} and let f = {(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)} be a function from A to B. State whether f is one-one or not.
If f : {5, 6} → {2, 3} and g : {2, 3} → {5, 6} are given by f = {(5, 2), (6, 3)} and g = {(2, 5), (3, 6)}, then find fog. [NCERT EXEMPLAR]
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be a function defined by
Let
\[f : R \to R\] be given by \[f\left( x \right) = x^2 - 3\] Then, \[f^{- 1}\] is given by
Which function is used to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not?
Set A has 3 elements and the set B has 4 elements. Then the number of injective mappings that can be defined from A to B is ______.
For sets A, B and C, let f: A → B, g: B → C be functions such that g o f is injective. Then both f and g are injective functions.
Let A = [–1, 1]. Then, discuss whether the following functions defined on A are one-one, onto or bijective:
k(x) = x2
Range of `"f"("x") = sqrt((1 - "cos x") sqrt ((1 - "cos x")sqrt ((1 - "cos x")....infty))`
Consider a set containing function A= {cos–1cosx, sin(sin–1x), sinx((sinx)2 – 1), etan{x}, `e^(|cosx| + |sinx|)`, sin(tan(cosx)), sin(tanx)}. B, C, D, are subsets of A, such that B contains periodic functions, C contains even functions, D contains odd functions then the value of n(B ∩ C) + n(B ∩ D) is ______ where {.} denotes the fractional part of functions)
Let f(x) be a polynomial of degree 3 such that f(k) = `-2/k` for k = 2, 3, 4, 5. Then the value of 52 – 10f(10) is equal to ______.
Which one of the following graphs is a function of x?
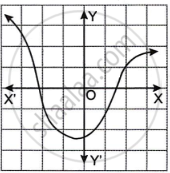 |
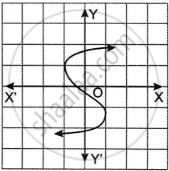 |
| Graph A | Graph B |
If f : R `rightarrow` R is defined by `f(x) = (2x - 7)/4`, show that f(x) is one-one and onto.
