Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State two factors upon which the rate of emission of thermions depends.
The S.I. unit of specific latent heat is ______.
During transformation of liquid phase to solid phase, the latent heat is ______.
When a liquid is getting converted into solid, the latent heat is ………………………………
Explain the following temperature Vs. time graph:
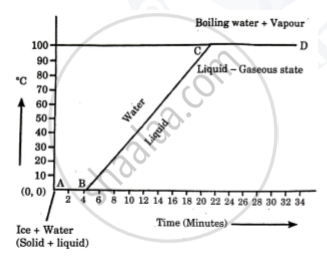
What is the name given to the energy absorbed during a phase change?
A substance changes from its solid state to the liquid state when heat is supplied to it. What name is given to heat absorbed by the substance.
Explain the meaning of the term latent heat. State its S. I. unit.
When 1 g of ice at 0 °C melts to form 1 g of water at 0 °C then, is the latent heat absorbed by the ice or given out by it?
Explain, why no tracks are left on the ice during ice skating?
Why does evaporation causes cooling and why is water used in hot water bottles?
What observation you will record and how will you determine the specific latent heat of fusion of ice?
Match the columns.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1) Specific latent heat of fusion | a) Air saturated with vapour |
| 2) Specific latent heat of vaporisation | b) Solid converts into liquid |
| 3) Dew point temperature | c) liquid converts into gas |
Write the name.
The phase in which solid substances are converted into liquid.
2875 J of heat is required to melt 115 g of lead at its melting point. Calculate the specific latent heat capacity of fusion of lead.
The amount of heat energy required to melt a given mass of a substance at its melting point without any rise in its temperature is called as the ______.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for a substance:
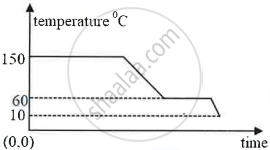
- State the temperatures at which the substance condenses.
- The temperature range in which the substance is in liquid state.
- Why do we prefer ice to ice-cold water for cooling a drink?
