Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When a nucleus at rest emits a beta particle, it is found that the velocities of the recoiling nucleus and the beta particle are not along the same straight line. How can this be possible in view of the principle of conservation of momentum?
उत्तर
In view of the principle of conservation of momentum, the given situation is possible because as a beta particle is ejected, another particle called an antineutrino is also ejected.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two bodies make an elastic head-on collision on a smooth horizontal table kept in a car. Do you expect a change in the result if the car is accelerated in a horizontal road because of the non inertial character of the frame? Does the equation "Velocity of separation = Velocity of approach" remain valid in an accelerating car? Does the equation "final momentum = initial momentum" remain valid in the accelerating car?
Use the definition of linear momentum from the previous question. Can we state the principle of conservation of linear momentum for a single particle?
Consider the following two statements:
(A) Linear momentum of a system of particles is zero.
(B) Kinetic energy of a system of particles is zero.
A bullet hits a block kept at rest on a smooth horizontal surface and gets embedded into it. Which of the following does not change?
A uranium-238 nucleus, initially at rest, emits an alpha particle with a speed of 1.4 × 107m/s. Calculate the recoil speed of the residual nucleus thorium-234. Assume that the mass of a nucleus is proportional to the mass number.
A man of mass 50 kg starts moving on the earth and acquires a speed 1.8 m/s. With what speed does the earth recoil? Mass of earth = 6 × 1024 kg.
A neutron initially at rest, decays into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. The ejected electron has a momentum of 1.4 × 10−26 kg-m/s and the antineutrino 6.4 × 10−27kg-m/s.
Find the recoil speed of the proton
(a) if the electron and the antineutrino are ejected along the same direction and
(b) if they are ejected along perpendicular directions. Mass of the proton = 1.67 × 10−27 kg.
A ball of mass 0.50 kg moving at a speed of 5.0 m/s collides with another ball of mass 1.0 kg. After the collision the balls stick together and remain motionless. What was the velocity of the 1.0 kg block before the collision?
A 60 kg man skating with a speed of 10 m/s collides with a 40 kg skater at rest and they cling to each other. Find the loss of kinetic energy during the collision.
A ball of mass m moving at a speed v makes a head-on collision with an identical ball at rest. The kinetic energy of the balls after the collision is three fourths of the original. Find the coefficient of restitution.
A block of mass 2.0 kg is moving on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity of 1.0 m/s (In the following figure) towards another block of equal mass kept at rest. The spring constant of the spring fixed at one end is 100 N/m. Find the maximum compression of the spring.

A bullet of mass 25 g is fired horizontally into a ballistic pendulum of mass 5.0 kg and gets embedded in it. If the centre of the pendulum rises by a distance of 10 cm, find the speed of the bullet.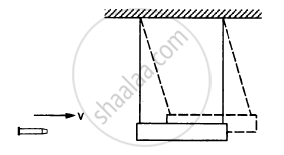
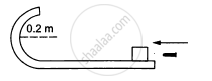
A bullet of mass 10 g moving horizontally at a speed of 50√7 m/s strikes a block of mass 490 g kept on a frictionless track as shown in figure. The bullet remains inside the block and the system proceeds towards the semicircular track of radius 0.2 m. Where will the block strike the horizontal part after leaving the semicircular track?
A metre stick is held vertically with one end on a rough horizontal floor. It is gently allowed to fall on the floor. Assuming that the end at the floor does not slip, find the angular speed of the rod when it hits the floor.
A uniform rod pivoted at its upper end hangs vertically. It is displaced through an angle of 60° and then released. Find the magnitude of the force acting on a particle of mass dm at the tip of the rod when the rod makes an angle of 37° with the vertical.
The following figure shows a rough track, a portion of which is in the form of a cylinder of radius R. With what minimum linear speed should a sphere of radius r be set rolling on the horizontal part so that it completely goes round the circle on the cylindrical part.

