Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why are carboxylic acids more acidic than alcohols or phenols although all of them have hydrogen atom attached to a oxygen atom \[\ce{(-O-H)}\]?
उत्तर
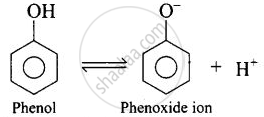
The aliphatic carboxylic acids are stronger acids than alcohols and phenols. The difference in the relative acidic strengths can be understood if we compare the resonance hybrids of carboxylate ion and ethoxide phenoxide ion.
\[\ce{RCOOH ⇌ RCOO- + H+}\]
\[\ce{ROH ⇌ RO- + H+}\]
The resonance hybrids may be represented as:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.............}\ce{O^{δ-}}\\
\phantom{.........}//\\
\ce{R - C}\\
\phantom{........}\backslash\backslash\\
\phantom{............}\ce{O^{δ-}}\\
\end{array}\]
Carboxylate ion
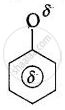
Phenoxide ion
\[\ce{RO-}\]
(No resonance)
The resonance hybrids may be represented as: Carboxylate ion Phenoxide ion (No resonance)
The electron charge on the carboxylate ion is more dispersed in comparison to the phenate ion since there are two electronegative oxygen atoms in carboxylate ion as compared to only one oxygen atom in phenoxide ion. In other words, the carboxylate ion is relatively more stable as compared to phenate ion. Thus, the release of H+ ion from carboxylic acid is comparatively easier or it behaves as a stronger acid than phenol.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How will you convert ethanal into the following compound?
But-2-enal
Write chemical equations of the following reaction :
Propanone is treated with dilute Ba (OH)2-.
Which product is formed when the compound  is treated with concentrated aqueous \[\ce{KOH}\] solution?
is treated with concentrated aqueous \[\ce{KOH}\] solution?
Assertion: Aromatic aldehydes and formaldehyde undergo Cannizaro reaction.
Reason: Aromatic aldehydes are almost as reactive as formaldehyde.
Convert the following:
Acetaldehyde to But-2-enal
Which of the following does not give aldol condensation reaction?
Assertion (A): The final product in Aldol condensation is always α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Reason (R): α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds are stabilised due to conjugation.

Identify A and B:
When acetaldehyde is treated with dilute NaOH, the following reaction is observed.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{2CH3 - CHO ->[dil.NaOH] CH3 - CH - CH2 - CHO}\\
\phantom{...............}|\\
\phantom{.................}\ce{OH}
\end{array}\]
- What are the functional groups in the product?
- Can another product be formed during the same reaction? (Deduce the answer by doing atomic audit of reactant and product).
- Is this an addition reaction or condensation reaction?
What is aldol condensation? Explain it with suitable examples.
