Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why are carboxylic acids more acidic than alcohols or phenols although all of them have hydrogen atom attached to a oxygen atom \[\ce{(-O-H)}\]?
उत्तर
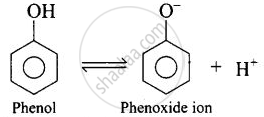
The aliphatic carboxylic acids are stronger acids than alcohols and phenols. The difference in the relative acidic strengths can be understood if we compare the resonance hybrids of carboxylate ion and ethoxide phenoxide ion.
\[\ce{RCOOH ⇌ RCOO- + H+}\]
\[\ce{ROH ⇌ RO- + H+}\]
The resonance hybrids may be represented as:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.............}\ce{O^{δ-}}\\
\phantom{.........}//\\
\ce{R - C}\\
\phantom{........}\backslash\backslash\\
\phantom{............}\ce{O^{δ-}}\\
\end{array}\]
Carboxylate ion
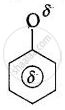
Phenoxide ion
\[\ce{RO-}\]
(No resonance)
The resonance hybrids may be represented as: Carboxylate ion Phenoxide ion (No resonance)
The electron charge on the carboxylate ion is more dispersed in comparison to the phenate ion since there are two electronegative oxygen atoms in carboxylate ion as compared to only one oxygen atom in phenoxide ion. In other words, the carboxylate ion is relatively more stable as compared to phenate ion. Thus, the release of H+ ion from carboxylic acid is comparatively easier or it behaves as a stronger acid than phenol.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give reasons Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
Why is alpha (α) hydrogen of carbonyl compounds acidic in nature?
Write chemical equations of the following reaction :
Benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated in the presence of `"Pd"/(BaSO_4)`
Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation?
(i) \[\ce{CH3 - CHO}\]
(ii) 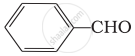
(iii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{}||\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH3}
\end{array}\]
(iv) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CHO}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
\end{array}\]
Assertion: The α-hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic.
Reason: The anion formed after the loss of α-hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
Identify A and B from the following reaction:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\phantom{}\ce{2CH3 - C = O ->[Ba(OH)2] A ->[Δ] B + H2O}
\end{array}\]
The major product of the following reaction is:
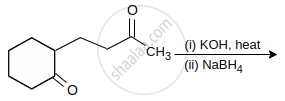
Explain Aldol condensation of ethanal.
Why is the α-hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones are acidic in nature?
Write a note on the aldol condensation reaction of acetaldehyde.
