Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why covalent compounds are different from ionic compounds?
उत्तर
Ionic compounds, on the other hand, are the compounds that are formed by the complete transfer of valence electrons between the constituent atoms. For example, a molecule of sodium chloride (NaCl) is formed when the sodium atom donates its one valence electron to the chlorine atom.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write any three features and give two examples of covalent compounds
What would be the electron-dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2?
What do you call the compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms?
State one test by which sodium chloride can be distinguished from sugar.
What type of bonding would you expect between Carbon and Chlorine?
Explain why, diamond is hard while graphite is soft (though both are made of carbon atoms).
Draw the electron-dot structure of NH3 and state the type of bonding.
A solid element X has four electrons in the outermost shell of its atom. An allotrope Y of this element is used as a dry lubricant in machinery and also in making pencil leads.
(a) What is element X?
(b) Name the allotrope Y.
(c) State whether allotrope Y is a good conductor or non-conductor of electricity.
(d) Name one use of allotrope Y (other than lubrication and pencil leads)
(e) Name two other allotropes of element X.
Give examples for the following:
Two liquid non polar compounds.
Fill in the blank from the choice given in bracket.
The compound that does not have a lone pair of electrons is ___________. (Water, Ammonia, carbon tetrachloride)
Which of the following is a common characteristic of a covalent compound?
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Covalent compounds are generally soluble in _________ solvents.
Name two carbon compounds used in day-to-day life.
Write scientific reason.
Carbon has the property of forming many compounds.
Explain covalent bond with example.
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
| \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{.........}\ce{H}\\ \phantom{.........}|\\ \ce{H - C ≡ C - C - H}\\ \phantom{.........}|\\ \phantom{.........}\ce{H} \end{array}\] |
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
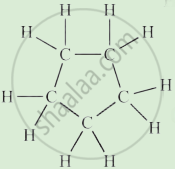 |
Give an example for each of the following statement.
Formation of coordinate covalent bond between NH3 ➝ BF3 molecules
Which of the following statements are usually correct for carbon compounds? These
- are good conductors of electricity
- are poor conductors of electricity
- have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
- do not have strong forces of attraction between their molecules.
Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because
- mineral acids are completely ionised
- carboxylic acids are completely ionised
- mineral acids are partially ionised
- carboxylic acids are partially ionised
