Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw the electron-dot structure of NH3 and state the type of bonding.
उत्तर
The electron-dot structure of NH3 is:
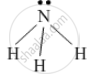
In NH3, each hydrogen atom shares its one electron with the nitrogen atom to form a covalent bond.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why covalent compounds are different from ionic compounds?
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Which of the following is a common characteristic of a covalent compound?
1) high melting point
2) consists of molecules
3) always soluble in water
4) Conducts electricity when it is in the molten state
Write any three features and give two examples of covalent compounds
Name the element whose one of the allotropic forms is buckminsterfullerene.
What do you call the compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms?
Fill in the blank in the following sentence:
The number of single covalent bonds in C2H2 molecule are ...........
How will you find out which of the water soluble compound A or B is ionic?
State one use of diamond which depends on its 'extraordinary brilliance' and one use of graphite which depends on its being 'black and quite soft'.
One of the following is not an allotrope of carbon. This is:
(a) diamond
(b) graphite
(c) cumene
(d) buckministerfullerene
State the type of bonding in the following molecule.
Water
Elements forming ionic compounds attain noble gas electronic configuration by either gaining or losing electrons from their valence shells. Explain giving reason why carbon cannot attain such a configuration in this manner to form its compounds. Name the type of bonds formed in ionic compounds and in the compounds formed by carbon. Also explain the reason why carbon compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity.
Explain the following briefly.
Pure water does not conduct electricity, but on adding sodium chloride to it, it starts conducting electricity.
Give examples for the following:
Two solid covalent compounds.
Electrons are getting added to an element Y:
Is Y getting oxidised or reduced?
Name two compounds that are covalent when taken pure but produce ions when dissolved in water.
Explain the following:
Polar covalent compounds conduct electricity?
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.....}|\\
\ce{H}\ce{H-C-H}\ce{H}\\
|\\
\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{......}\ce{C - H}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\]
The electron dot structure of chlorine molecule is:
