Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw the electron-dot structure of NH3 and state the type of bonding.
उत्तर
The electron-dot structure of NH3 is:
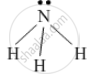
In NH3, each hydrogen atom shares its one electron with the nitrogen atom to form a covalent bond.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why covalent compounds are different from ionic compounds?
What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur? (Hint – the eight atoms of sulphur are joined together in the form of a ring.)
Give appropriate scientific reasons for Carbon tetrachloride does not conduct electricity.
Write any three features and give two examples of covalent compounds
What is the difference between ionic compounds and covalent compounds?
For each compound mentioned above give the formulae of ions formed in aqueous solution.
State the type of bonding in the following molecule.
Hydroxyl ion
Elements forming ionic compounds attain noble gas electronic configuration by either gaining or losing electrons from their valence shells. Explain giving reason why carbon cannot attain such a configuration in this manner to form its compounds. Name the type of bonds formed in ionic compounds and in the compounds formed by carbon. Also explain the reason why carbon compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity.
Explain the following term with example.
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Molecular formula of Propane is C3H8 , write the structural formula of propane.
Explain the following:
Non-polar covalent compounds are insoluble in water.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
Condition favorable for formation of a covalent bond is
Fill in the blank from the choice given in bracket.
The compound that does not have a lone pair of electrons is ___________. (Water, Ammonia, carbon tetrachloride)
State the type of bond formed, and draw Lewis structure of water.
Explain the following:
Water is a polar covalent molecule.
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
| \[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\ |\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\ |\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H} \end{array}\] |
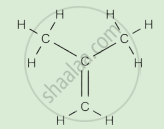
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
 |
Give an example for each of the following statement
A compound in which two Covalent bonds are formed.
______ is an example of a covalent compound having a high melting point.
Molecular reactions are ______ in the covalent compound.
