Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two samples A and B, of the same gas have equal volumes and pressures. The gas in sample A is expanded isothermally to double its volume and the gas in B is expanded adiabatically to double its volume. If the work done by the gas is the same for the two cases, show that γ satisfies the equation 1 − 21−γ = (γ − 1) ln2.
उत्तर
Let,
Initial pressure of the gas = P1
Initial volume of the gas = V1
Final pressure of the gas= P2
Final volume of the gas = V2
Given, V2 = 2 V1, for each case.
In an isothermal expansion process,
work done = `"n""R""T"_1 "l""n" "V"_2/"V"_1" `
Adiabatic work done,
`"W" = ("P"_1"V"_1 - "P"_2"V"_2)/ (gamma -1 )`
It is given that same work is done in both cases.
So,
`"n""R""T"_1 "l""n" ("V"_2/"V"_1) =( "P"_1 "V"_1 - "P"_2"V"_2)/ (gamma -1)` ..(1)
In an adiabatic process,
`"P"_2 = "P"_1 ("V"_1/"V"_2)^gamma ="P"_1(1/2)^gamma`
From eq (1),
`"n""R""T"_1 "l""n" 2 = ("P"_1"V"_1(1-1/2^gamma xx 2)) /(gamma -1)`
and nRT1 = P1V1
So, ln 2 =` (1 - 1/(2^gamma) . 2)/ (gamma -1)`
Or (γ − 1) ln 2 = 1 − 21−γ
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following quantities is zero on an average for the molecules of an ideal gas in equilibrium?
The average momentum of a molecule in a sample of an ideal gas depends on
Let Q and W denote the amount of heat given to an ideal gas and the work done by it in an adiabatic process.
(a) Q = 0
(b) W = 0
(c) Q = W
(d) Q ≠ W
A rigid container of negligible heat capacity contains one mole of an ideal gas. The temperature of the gas increases by 1° C if 3.0 cal of heat is added to it. The gas may be
(a) helium
(b) argon
(c) oxygen
(d) carbon dioxide
A vessel containing one mole of a monatomic ideal gas (molecular weight = 20 g mol−1) is moving on a floor at a speed of 50 m s−1. The vessel is stopped suddenly. Assuming that the mechanical energy lost has gone into the internal energy of the gas, find the rise in its temperature.
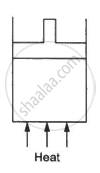
The figure shows a cylindrical container containing oxygen (γ = 1.4) and closed by a 50-kg frictionless piston. The area of cross-section is 100 cm2, atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa and g is 10 m s−2. The cylinder is slowly heated for some time. Find the amount of heat supplied to the gas if the piston moves out through a distance of 20 cm.
The ratio of the molar heat capacities of an ideal gas is Cp/Cv = 7/6. Calculate the change in internal energy of 1.0 mole of the gas when its temperature is raised by 50 K (a) keeping the pressure constant (b) keeping the volume constant and (c) adiaba
An ideal gas (Cp / Cv = γ) is taken through a process in which the pressure and the volume vary as p = aVb. Find the value of b for which the specific heat capacity in the process is zero.
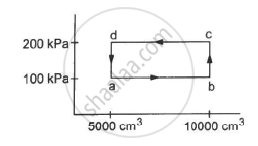
Half mole of an ideal gas (γ = 5/3) is taken through the cycle abcda, as shown in the figure. Take `"R" = 25/3"J""K"^-1 "mol"^-1 `. (a) Find the temperature of the gas in the states a, b, c and d. (b) Find the amount of heat supplied in the processes ab and bc. (c) Find the amount of heat liberated in the processes cd and da.
An ideal gas at pressure 2.5 × 105 Pa and temperature 300 K occupies 100 cc. It is adiabatically compressed to half its original volume. Calculate (a) the final pressure (b) the final temperature and (c) the work done by the gas in the process. Take γ = 1.5
Consider a given sample of an ideal gas (Cp/Cv = γ) having initial pressure p0 and volume V0. (a) The gas is isothermally taken to a pressure p0/2 and from there, adiabatically to a pressure p0/4. Find the final volume. (b) The gas is brought back to its initial state. It is adiabatically taken to a pressure p0/2 and from there, isothermally to a pressure p0/4. Find the final volume.
An ideal gas of density 1.7 × 10−3 g cm−3 at a pressure of 1.5 × 105 Pa is filled in a Kundt's tube. When the gas is resonated at a frequency of 3.0 kHz, nodes are formed at a separation of 6.0 cm. Calculate the molar heat capacities Cp and Cv of the gas.
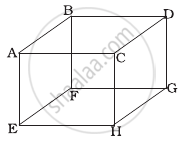
1 mole of an ideal gas is contained in a cubical volume V, ABCDEFGH at 300 K (Figure). One face of the cube (EFGH) is made up of a material which totally absorbs any gas molecule incident on it. At any given time ______.
The container shown in figure has two chambers, separated by a partition, of volumes V1 = 2.0 litre and V2 = 3.0 litre. The chambers contain µ1 = 4.0 and µ2 = 5.0 moles of a gas at pressures p1 = 1.00 atm and p2 = 2.00 atm. Calculate the pressure after the partition is removed and the mixture attains equilibrium.
| V1 | V2 |
| µ1, p1 | µ2 |
| p2 |
We have 0.5 g of hydrogen gas in a cubic chamber of size 3 cm kept at NTP. The gas in the chamber is compressed keeping the temperature constant till a final pressure of 100 atm. Is one justified in assuming the ideal gas law, in the final state?
(Hydrogen molecules can be consider as spheres of radius 1 Å).
