Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write briefly the important processes that occur during the formation of p−n junction. With the help of necessary diagrams, explain the term 'barrier potential'.
उत्तर
A thin p-type semiconductor wafer is taken and a part of it is converted into n-si by adding a small quantity of pentavalent impurity. The wafer now contains a p-region and an n-region and a metallurgical junction between p and n region.
The n-type semiconductor has more concentration of electrons than hole and p-type semiconductor has more concentration of holes than electrons. So, the holes diffuse from the p-side to the n-side and electrons diffuse from the n-side to the p-side. When an electron diffuses from the n-side to the p-side, it leaves an ionised donor behind it in the n-region. The ionised donor, which is positively charged, is immobile as it is bounded by surrounding atoms. Therefore, a layer of positive charge is developed on n-side of the junction. Similarly, when holes diffuse from p-side to n-side, they leave an ionised acceptor behind them in the p-region. The ionised acceptor, which is negatively charged, is also immobile due to surrounding atoms. Thus, a layer of negative charge is developed on the p-side of the junction.
This space region on both the sides of p-n junction, devoid of any charge carrier, will form a region called depletion region.
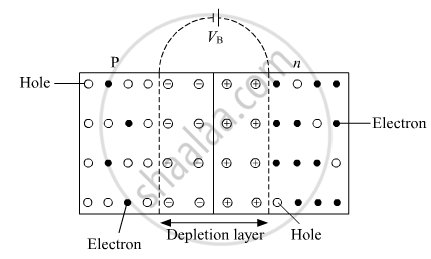
Due to the positive charge region on n-side of the junction and negative charge on p-side of the junction, an electric electric field is set up across the junction from the positive charge towards the negative charge. This electric field sets up a barrier potential at the junction that opposes diffusion of majority charge carriers into opposite regions. As the diffusion process continues, the space-charge regions across the junction extend. The strength of the electric field increases; thereby, increasing the drift current . This process continues until the diffusion current becomes equal to the drift current. When this stage is reached, the movement of majority carriers across the junction stops. Now the junction is in equilibrium state. At this stage, the potential barrier across the p-n junction has maximum value \[V_B\].
It means that he barrier voltage stops the diffusion of majority charge carriers from p- to n-region across the junction and vice versa. This potential acts as a barrier and, hence, is known as barrier potential.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Meeta's father was driving her to school. At the traffic signal, she noticed that each traffic light was made of many tiny lights instead of a single bulb. When Meeta asked this question to her father, he explained the reason for this.
Answer the following questions based on above information:
(i) What were the values displayed by Meeta and her father?
(ii) What answer did Meeta's father give?
(iii) What are the tiny lights in traffic signals called and how do these operate?
If a small voltage is applied to a p-n junction diode, how will the barrier potential be affected when it is (i) forward biased
Using the necessary circuit diagrams, show how the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction are obtained in
Forward biasing
How are these characteristics made use of in rectification?
Sunil and his parents were travelling to their village in their car. On the way his mother noticed some grey coloured panels installed on the roof of a low building. She enquired from Sunil what those panels were and Sunil told his mother that those were solar panels.
(a) What were the values displayed by Sunil and his mother? State one value for each.
(b) In what way would the use of solar panels prove to be very useful?
(c) Name the semiconductor device used in solar panels. Briefly explain with the help of a diagram, how this device works
How is a photodiode fabricated?
Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier using p-n junction diode.
Explain its working and show the output, input waveforms.
Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias. How is photodiode used to measure light intensity?
Explain how a potential barrier is developed in a p-n junction diode.
Pressure P varies as P = `alpha/beta "exp" (- (alpha x)/"k"_"BT")`, where x denotes the distance, kB is the Boltzmann's constant, T is the absolute temperature and α and β are constant. The dimension of β is ______.
How can a photodiode be used to measure light intensity?
