Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2014-2015
Date: मार्च 2015
Advertisements
Why does the Sun look reddish at sunset or sunrise ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
The power factor of an a.c. circuit is 0.5. What is the phase difference between voltage and current in this circuit ?
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Is it necessary for a transmitting antenna to be at the same height as that of receiving antenna for LOS communication ?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Plot a graph showing the variation of resistivity of a conductor with temperature.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Write the expression for the torque \[\vec{\tau}\] acting on a dipole of dipole moment \[\vec{p}\] placed in an electric field \[\vec{E}\].
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Write the β-decay of tritium in symbolic form.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Why is it experimentally found difficult to detect neutrinos in this process ?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (11/3) Ω?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (11/5) Ω?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
The V − I characteristic of a silicon diode is as shown in the figure. Calculate the resistance of the diode at (i) I = 15 mA and (ii) V= −10 V.

Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
How does the refractive index of a transparent medium depend on the wavelength of incident light used ?
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Velocity of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s and in air is 3 × 108 m/s. If the ray of light passes from glass to air, calculate the value of critical angle.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
An equiconvex lens of focal length 'f' is cut into two identical plane convex lenses. How will the power of each part be related to the focal length of the original lens ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A double convex lens of + 5 D is made of glass of refractive index 1.55 with both faces of equal radii of curvature. Find the value of its radius of curvature.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
The kinetic energy of the electron orbiting in the first excited state of hydrogen atom is 3.4 eV. Determine the de Broglie wavelength associated with it.
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Write briefly the important processes that occur during the formation of p−n junction. With the help of necessary diagrams, explain the term 'barrier potential'.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Advertisements
A beam of monochromatic radiation is incident on a photosensitive surface. Answer the following question giving reason :
Do the emitted photoelectrons have the same kinetic energy?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
A beam of monochromatic radiation is incident on a photosensitive surface. Answer the following question giving reason :
Does the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons depend on the intensity of incident radiation?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
A beam of monochromatic radiation is incident on a photosensitive surface. Answer the following question giving reason :
On what factors does the number of emitted photoelectrons depend?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
What is an 'integrated circuit (I.C.) ?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Distinguish between (i) linear I.C. and (ii) digital I.C.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Identify the equivalent gate for the following circuit and write its truth table.
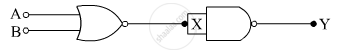
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Why does a galvanometer when connected in series with a capacitor show a momentary deflection, when it is being charged or discharged?
How does this observation lead to modifying the Ampere's circuital law?
Hence write the generalised expression of Ampere's law.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
In the given circuit in the steady state, obtain the expressions for (a) the potential drop (b) the charge and (c) the energy stored in the capacitor, C.

Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
A circular coil of radius 10 cm, 500 turns and resistance 200 Ω is placed with its plane perpendicular to the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field. It is rotated about its vertical diameter through 180° in 0.25 s. Estimate the magnitude of the emf and current induced in the coil. (Horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field at the place is 3.0 ✕ 10−5 T).
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Using Rydberg formula, calculate the longest wavelength belonging to Lyman and Balmer series. In which region of hydrogen spectrum do these transitions lie?
[Given R = 1.1 ✕ 107 m−1]
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
Why cannot two independent monochromatic sources produce sustained interference pattern?
Deduce, with the help of Young's arrangement to produce interference pattern, an expression for the fringe width.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Answer the following question :
Define 'bandwidth' and describe briefly its importance in communicating signals ?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Answer the following question :
Distinguish between digital and analogue signals.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Answer the following question :
Write the functions of transducer and repeater ?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Four charges +q, −q, +q and −q are to be arranged respectively at the four corners of a square ABCD of side 'a'.
(a) Find the work required to put together this arrangement.
(b) A charge q0 is brought to the centre of the square, the four charges being held fixed. How much extra work is needed to do this ?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Three point charges +q each are kept at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 'l'. Determine the magnitude and sign of the charge to be kept at its centroid so that the charges at the vertices remain in equilibrium.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Advertisements
An electron moving horizontally with a velocity of 4 ✕ 104 m/s enters a region of uniform magnetic field of 10−5 T acting vertically upward as shown in the figure. Draw its trajectory and find out the time it takes to come out of the region of magnetic
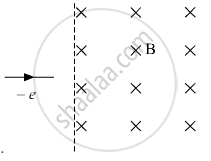
field.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2 A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform magnetic field B. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A plane wavefront propagating in a medium of refractive index 'μ1' is incident on a plane surface making the angle of incidence 'i' as shown in the figure. It enters into a medium of refractive index 'μ2' (μ2 > μ1). Use Huygens' construction of secondary wavelets to trace the propagation of the refracted wavefront. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
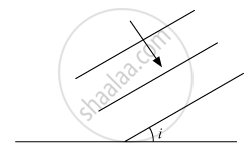
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Sushil is in the habit of charging his mobile and then leaving the charger connected through the mains with the switch on. When his sister Asha pointed it out to him, he replied there was no harm as the mobile had been disconnected. Asha then explained to him and convinced him, how the energy was still being wasted as the charger was continuously consuming energy.
Answer the following questions :
(a) What values did Asha display in convincing her brother?
(b) What measures, in your view, should be adopted to minimise the wastage of electric energy in your households?
(c) Imagine an electric appliance of 2 W, left connected to the mains for 20 hours. Estimate the amount of electrical energy wasted.
Chapter:
A small conducting sphere of radius 'r' carrying a charge +q is surrounded by a large concentric conducting shell of radius Ron which a charge +Q is placed. Using Gauss's law, derive the expressions for the electric field at a point 'x'
(i) between the sphere and the shell (r < x < R),
(ii) outside the spherical shell.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Show that if we connect the smaller and the outer sphere by a wire, the charge q on the former will always flow to the latter, independent of how large the charge Q is.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Consider a system of n charges q1, q2, ... qn with position vectors `vecr_1,vecr_2,vecr_3,...... vecr_n`relative to some origin 'O'. Deduce the expression for the net electric field`vec E` at a point P with position vector `vecr_p,`due to this system of charges.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Find the resultant electric field due to an electric dipole of dipole moment, 2aq, (2a being the separation between the charges ±± q) at a point distant 'x' on its equator.
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Draw a ray diagram showing the image formation of a distant object by a refracting telescope ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Define the magnifying power?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write the two important factors considered to increase the magnifying power?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Describe briefly the two main limitations and explain how far these can be minimized in a reflecting telescope ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Draw a ray diagram showing image formation in a compound microscope ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Define the term 'limit of resolution'?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
name the factors on which 'limit of resolution' depends ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
How is 'limit of resolution' related to resolving power of a microscope ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Suggest two ways by which the resolving power of a microscope can be increased?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
"A telescope resolves whereas a microscope magnifies." Justify this statement ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write any two important points of similarities and differences each between Coulomb's law for the electrostatic field and Biot-Savart's law of the magnetic field ?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Use Biot-Savart's law to find the expression for the magnetic field due to a circular loop of radius 'r' carrying current 'I', at its centre ?
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
What are eddy currents?
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
How are eddy currents produced ?
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Describe briefly three main useful application of eddy currents ?
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2014 - 2015
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2015 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
