Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A small conducting sphere of radius 'r' carrying a charge +q is surrounded by a large concentric conducting shell of radius Ron which a charge +Q is placed. Using Gauss's law, derive the expressions for the electric field at a point 'x'
(i) between the sphere and the shell (r < x < R),
(ii) outside the spherical shell.
उत्तर १
Consider a sphere of radius r with centre O surrounded by a large concentric conducting shell of radius R.
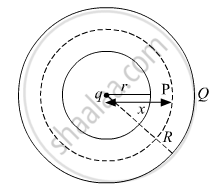
To calculate the electric field intensity at any point P, where OP = x, imagine a Gaussian surface with centre O and radius x, as shown in the figure given above.
The total electric flux through the Gaussian surface is given by
`ø = oint_s Eds = E oint_s \ ds`
Now,
`oint \ ds = 4πx^2`
`∴ø = E xx 4πx^2 ....... (1) `
Since the charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface is q, according to Gauss's theorem,
`ø = q/ε_0 ....... (2)`
From (i) and (ii), we get
` E xx 4πx^2 = q/ε_0 `
⇒`E = q/(4πε_0x^2 )`
उत्तर २
(1) Consider a sphere of radius r with centre O surrounded by a large concentric conducting shell of radius R.

To calculate the electric field intensity at any point P, where OP = x, imagine a Gaussian surface with centre O and radius x, as shown in the figure given above.
The total electric flux through the Gaussian surface is given by
`ø = oint_s Eds = E oint_s \ ds`
Now,
`oint \ ds = 4πx^2`
`∴ø = E xx 4πx^2 ....... (1) `
Since the charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface is q, according to Gauss's theorem,
`ø = q/ε_0 ....... (2)`
From (i) and (ii), we get
` E xx 4πx^2 = q/ε_0 `
⇒`E = q/(4πε_0x^2 )`
(2)
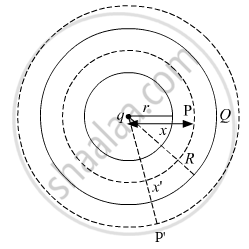
To calculate the electric field intensity at any point P', where point P' lies outside of the spherical shell, imagine a Gaussian surface with centre O and radius x', as shown in the figure given above.
According to Gauss's theorem,
` E' xx 4πx^'2 = (q+Q)/ε_0 `
⇒`E = (q+Q)/(4πx'^ 2 )`
As the charge always resides only on the outer surface of a conduction shell, the charge flows essentially from the sphere to the shell when they are connected by a wire. It does not depend on the magnitude and sign of charge Q.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs and of magnitude 17.0 × 10−22 C/m2. What is E:
- in the outer region of the first plate,
- in the outer region of the second plate, and
- between the plates?
Find the ratio of the potential differences that must be applied across the parallel and series combination of two capacitors C1 and C2 with their capacitances in the ratio 1 : 2 so that the energy stored in the two cases becomes the same.
Using Gauss's law in electrostatics, deduce an expression for electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet. If another identical sheet is placed parallel to it, show that there is no electric field in the region between the two sheets ?
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a convex spherical surface of radius of curvature R, which separates the two media of refractive indices n1 and n2 (n2 > n1). Draw the ray diagram and deduce the relation between the object distance (u), image distance (v) and the radius of curvature (R) for refraction to take place at the convex spherical surface from rarer to denser medium.
Using Gauss’ law deduce the expression for the electric field due to a uniformly charged spherical conducting shell of radius R at a point
(i) outside and (ii) inside the shell.
Plot a graph showing variation of electric field as a function of r > R and r < R.
(r being the distance from the centre of the shell)
Using Gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the distance from it.
A rubber balloon is given a charge Q distributed uniformly over its surface. Is the field inside the balloon zero everywhere if the balloon does not have a spherical surface?
A thin, metallic spherical shell contains a charge Q on it. A point charge q is placed at the centre of the shell and another charge q1 is placed outside it as shown in the following figure . All the three charges are positive. The force on the charge at the centre is ____________.
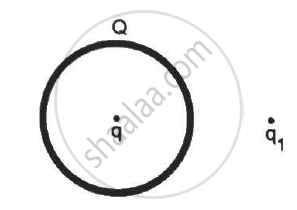
Find the flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius R due to a charge of 10−7 C at the centre and another equal charge at a point 2R away from the centre in the following figure.