Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (11/3) Ω?
उत्तर
The resistance of the given resistors is,
R1 = 1 Ω, R2 = 2 Ω, R3 = 3 Ω
Equivalent resistance, R' = `11/3` Ω
Consider the following combination of the resistors.
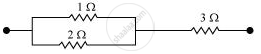
Equivalent resistance of the circuit is given by,
R' = `(2 xx 1)/(2 + 1) + 3`
= `2/3 + 3`
= `11/3` Ω
संबंधित प्रश्न
Kirchhoff's voltage law and current law are respectively in accordance with the conservation of .................................. .
- charge and momentum
- charge and energy
- energy and charge
- energy and momentum
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in electric networks. How are there rules justified?
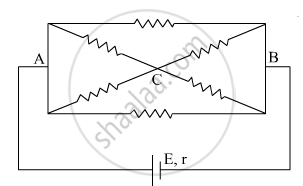
The current is drawn from a cell of emf E and internal resistance r connected to the network of resistors each of resistance r as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for
- the current draw from the cell and
- the power consumed in the network.
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (11/5) Ω?
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of 6 Ω?
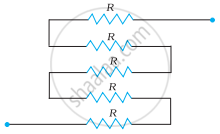
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
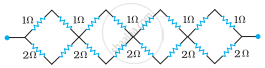
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
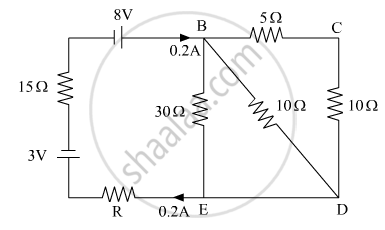
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points B and E?
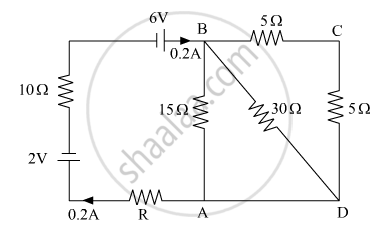
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points A and B?
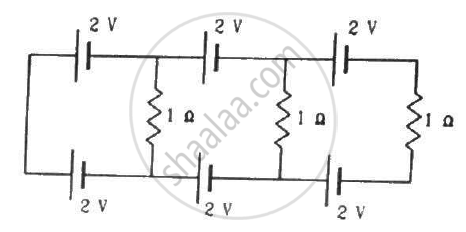
In the given circuit, assuming point A to be at zero potential, use Kirchhoff’s rules to determine the potential at point B.

Find the circuit in the three resistors shown in the figure.
A capacitor of capacitance 8.0 μF is connected to a battery of emf 6.0 V through a resistance of 24 Ω. Find the current in the circuit (a) just after the connections are made and (b) one time constant after the connections are made.
Solve the following question.
Using Kirchhoff’s rules, calculate the current through the 40 Ω and 20 Ω resistors in the following circuit.

How the emf of two cells are compared using potentiometer?
A potentiometer wire has a length of 4 m and resistance of 20 Ω. It is connected in series with resistance of 2980 Ω and a cell of emf 4 V. Calculate the potential along the wire.
Two cell of 1.25 V and 0.75 V are connected parallel. The effective voltage will be:-
In a meter bridge the point D is a neutral point (Figure).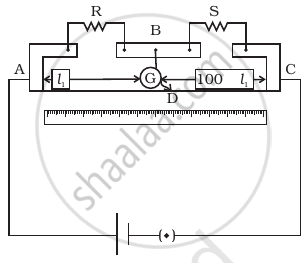
- The meter bridge can have no other neutral point for this set of resistances.
- When the jockey contacts a point on meter wire left of D, current flows to B from the wire.
- When the jockey contacts a point on the meter wire to the right of D, current flows from B to the wire through galvanometer.
- When R is increased, the neutral point shifts to left.
Power P is to be delivered to a device via transmission cables having resistance RC. If V is the voltage across R and I the current through it, find the power wasted and how can it be reduced.
The circuit in figure shows two cells connected in opposition to each other. Cell E1 is of emf 6V and internal resistance 2Ω; the cell E2 is of emf 4V and internal resistance 8Ω. Find the potential difference between the points A and B.
