Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (11/5) Ω?
उत्तर
Equivalent resistance, R' = `11/5` Ω
Consider the following combination of the resistors.
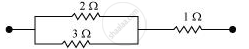
Equivalent resistance of the circuit is given by,
R' = `(2 xx 3)/(2 + 3) + 1`
= `6/5 + 1`
= `11/5` Ω
संबंधित प्रश्न
Kirchhoff's junction law is equivalent to .............................
(a) conservation of energy.
(b) conservation of charge
(c) conservation of electric potential
(d) conservation of electric flux
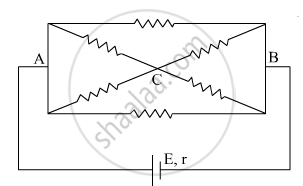
The current is drawn from a cell of emf E and internal resistance r connected to the network of resistors each of resistance r as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for
- the current draw from the cell and
- the power consumed in the network.
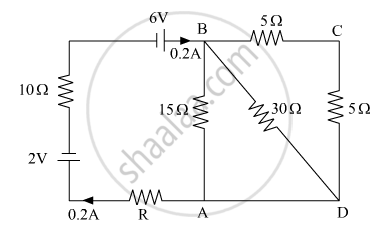
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points A and B?
In the given circuit, assuming point A to be at zero potential, use Kirchhoff’s rules to determine the potential at point B.

How the emf of two cells are compared using potentiometer?
A potentiometer wire has a length of 4 m and resistance of 20 Ω. It is connected in series with resistance of 2980 Ω and a cell of emf 4 V. Calculate the potential along the wire.
The instrument for the accurate measurement of the e.m.f of a cell is ______.
Assertion: Kirchhoff’s junction rule follows from conservation of charge.
Reason: Kirchhoff’s loop rule follows from conservation of momentum.
In a meter bridge the point D is a neutral point (Figure).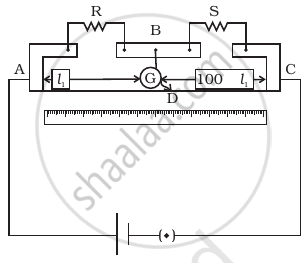
- The meter bridge can have no other neutral point for this set of resistances.
- When the jockey contacts a point on meter wire left of D, current flows to B from the wire.
- When the jockey contacts a point on the meter wire to the right of D, current flows from B to the wire through galvanometer.
- When R is increased, the neutral point shifts to left.
Derive the equation of the balanced state in a Wheatstone bridge using Kirchhoff’s laws.
