Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write scientific reason.
Use a pressure cooker to cook food in cold air.
उत्तर
- Normally, in cold air, more heat energy needs to be supplied to attain high temperatures required for cooking food. It also consumes more time.
- Whereas, pressure cooker operates by giving out the air within the cooker and trapping steam produced from the liquid, (mostly water) boiling inside.
- Due to high internal pressure, boiling point of liquid increases and liquid boils at temperature higher than its boiling point.
- The increased boiling point allows more absorption of heat by liquid and steam formed is superheated causing food to get cooked quickly.
Hence, it is advisable to use a pressure cooker to cook food in cold air.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
1 g ice of 0℃ melts to form 1 g water at 0℃. State whether the latent heat is absorbed or given out by ice.
Which has more heat: 1 g ice at 0℃ or 1g water 0℃? Give reason.
A molten metal of mass 150 g is kept at its melting point 800℃. When it is allowed to freeze at the same temperature, it gives out 75,000 J of heat energy.
- What is the specific latent heat of the metal?
- If the specific heat capacity of metal is 200 J kg-1 K-1, how much additional heat energy will the metal give out in cooling to -50℃?
A refrigerator converts 100g of water at 20℃ to ice at – 10℃ in 73.5 min. Calculate the average rate of heat extraction in watt. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.2 J kg-1 K-1, specific latent heat of ice is 336 J g-1 and the specific heat capacity of ice is 2.1 J kg-1 K-1.
Calculate the total amount of heat energy required to convert 100 g of ice at −10℃ completely into water at 100℃. Specific heat capacity of ice = 2.1 J g-1 K-1, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1K-1, specific latent heat of ice = 336 J g-1.
Explain the following temperature vs time graph.

Explain the following temperature vs time graph.
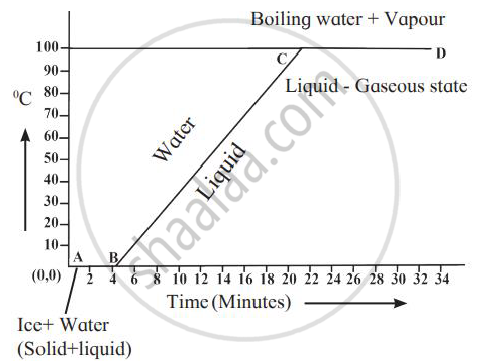
A substance changes from its solid state to the liquid state when heat is supplied to it. What name is given to heat absorbed by the substance.
Define specific latent heat of vaporization of a substance.
When 1 g of ice at 0 °C melts to form 1 g of water at 0 °C then, is the latent heat absorbed by the ice or given out by it?
Why water get cooled in a ‘Surahi’ in hot season?
Define the term ‘specific latent heat of fusion’ of a substance.
State two advantages of the high specific latent heat capacity of steam, which is about 226 × 104 J/kg?
Specific latent heat of vaporisation : J/kg : : specific heat : _______
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Match the columns.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1) Specific latent heat of fusion | a) Air saturated with vapour |
| 2) Specific latent heat of vaporisation | b) Solid converts into liquid |
| 3) Dew point temperature | c) liquid converts into gas |
For the same mass of ice and ice-cold water, why does ice produce more cooling than ice-cold water?
The amount of heat energy required to melt a given mass of a substance at its melting point without any rise in its temperature is called as the ______.
