Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Chemical Bonding
3: Acids, Bases and Salts
4: Analytical Chemistry: Uses of Ammonium Hydroxide and Sodium Hydroxide
5: Mole concept and Stoichiometry
6: Electrolysis
7: Metallurgy
▶ 8: Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride
9: Study of Compounds - Ammonia
10: Study of Compounds - Nitric Acid
11: Sulphuric Acid
12: Organic Chemistry
13: Practical Work
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-10-icse_6:654d3cd91177441db9833c3c89eccd66.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of CISCE Selina for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE 8 Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride Exercise 8 [Pages 147 - 149]
Draw a labelled diagram for the laboratory preparation of hydrogen chloride gas and answer the following.
- Name the acid used. Why is this particular acid preferred to other acids?
- Give the balanced equation for the reaction.
- Name the drying agent used in drying hydrogen chloride gas.
- Phosphorous pentoxide and calcium oxide are good drying agents, but they cannot be used to dry hydrogen chloride gas. Why?
- Why is the direct absorption of \[\ce{HCl}\] gas in water not feasible?
- What arrangement is done to dissolve \[\ce{HCl}\] gas in the water?
Explain why anhydrous \[\ce{HCl}\] is a poor conductor while aqueous \[\ce{HCl}\] is an excellent conductor.
Explain why when the stopper of a bottle full of hydrogen chloride gas is opened, there are fumes in the air.
Explain why a solution of hydrogen chloride in water turns blue litmus red and conducts electricity, while a solution of the same gas in toluene:
- has no effect on litmus, and
- does not conduct electricity.
Explain why thick white fumes are formed when a glass rod dipped in \[\ce{NH4OH}\] is brought near the mouth of a bottle full of \[\ce{HCl}\] gas.
Explain why dry hydrogen chloride gas does not affect a dry strip of blue litmus paper but it turns red in the presence of a drop of water.
Explain why hydrogen chloride gas is not collected over water.
The given set up in the figure is for the preparation of an acid.
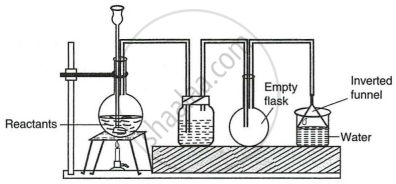
- Name the acid prepared by this method.
- Name the reactants used.
- Why an empty flask is used?
- What is the drying agent used? Why is this drying agent chosen?
- What is the role of the inverted funnel in the arrangement?
- Name the experiment illustrated below.
- State the colour of the water that has entered the round-bottomed flask.
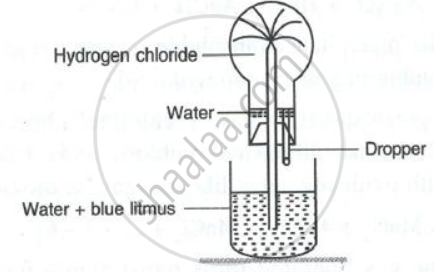
What property of hydrogen chloride is demonstrated when it is collected by downward delivery (Upward displacement)?
Name an element which reacts with hydrogen to form a compound which is strongly acidic in water.
Explain why dilute hydrochloric acid cannot be concentrated by boiling beyond 22.2%.
How will you prove that hydrochloric acid contains
- hydrogen
- chlorine?
Write equations for the reactions.
Name a black metallic oxide which reacts with hydrochloric acid to give a coloured solution.
Name two colourless gases, which when mixed, produce a white solid.
Name two gases which chemically combine to form a liquid.
Name a chloride which is solube in excess of ammonium hydroxide
Name the chemical in which gold can be dissolved.
Name the experiment which demonstrates that hydrogen chloride is soluble in water.
Name the gas produced when chlorine water is exposed to sunlight.
Solution A reacts with an acid B (which gives greenish yellow gas on reacting with oxidizing agents like \[\ce{Pb3O4}\]) to give white precipitate C insoluble in nitric acid but soluble in ammonium hydroxide. Name A, B and C.
Complete and balance the following reaction, state whether dilute or conc. acid is used.
\[\ce{NH4OH + HCl -> \underline{\phantom{..........}}}\].
Complete and balance the following reaction, state whether dilute or conc. acid is used.
\[\ce{NaHSO3 + HCl ->}\]
Complete and balance the following reaction, state whether dilute or conc. acid is used.
\[\ce{Pb(NO3)2 + HCl ->}\]
Complete and balance the following reaction, state whether dilute or conc. acid is used.
\[\ce{Pb3O4 + HCl ->}\]
How will the action of dilute hydrochloric acid enable you to distinguish between sodium carbonate and sodium sulphite?
How will the action of dilute hydrochloric acid enable you to distinguish between sodium thiosulphate and sodium sulphite?
Give three distinct test [apart from using an indicator] you would carry out with solution of \[\ce{HCl}\] to illustrate the typical properties of an acid.
\[\ce{MnO2}\], \[\ce{PbO2}\] and red lead react with \[\ce{conc. HCl}\] acid liberates \[\ce{Cl2}\].
What is the common property being shown by these metal oxides?
State which of the two a solution of HCl in water or in toluene is an electrolyte. Explain.
Convert two soluble metallic nitrates to insoluble metallic chlorides using \[\ce{dil. HCl}\].
Convert hydrochloric acid to nascent chlorine.
A solution of hydrogen chloride in water is prepared. The following substances are added to separate portions of the solution:
| S. No. | Substances added | Gas evolved | Odour |
| 1. | Calcium carbonate | _________ | _________ |
| 2. | Magnesium ribbon | _________ | _________ |
| 3. | Manganese (IV) oxide with heating | _________ | _________ |
| 4. | Sodium sulphide | _________ | _________ |
State the composition of aqua regia. State which component is the oxidizing agent in aqua regia.
Write an equation for the reaction of hydrochloric acid on the silver nitrate solution.
Write an equation for the reaction of hydrochloric acid on magnesium foil.
Write an equation for the reaction of hydrochloric acid on caustic soda solution.
Write an equation for the reaction of hydrochloric acid on zinc carbonate.
Write an equation for the reaction of hydrochloric acid on manganese (IV) oxide.
Write an equation for the reaction of hydrochloric acid on copper oxide.
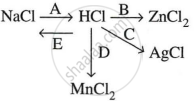
Study the flow chart and give balanced equations with conditions for the conversions A, B, C, D and E.
Write the balanced equation for the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid with the following:
Iron
Write the balanced equation for the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid with the following:
Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Write the balanced equation for the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid with the following:
Iron (II) sulphide
Write the balanced equation for the reaction of dilute hydrochloric acid with the following:
Magnesium sulphite
Write observation:
Lead nitrate solution is mixed with dilute hydrochloric acid and heated.
Write observation:
A small piece of zinc is added to dilute hydrochloric acid.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
The drying agent used to dry \[\ce{HCl}\] gas is ______.
\[\ce{Conc. H2SO4}\]
\[\ce{ZnO}\]
\[\ce{Al2O3}\]
\[\ce{CaO}\]
When sodium chloride is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid below 200°C, one of the products formed is ________.
sodium hydrogen sulphate
sodium sulphate
chlorine
Aqua regia is a mixture of ______.
Dilute hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid
Concentrated hydrochloric acid and dilute nitric acid
Concentrated hydrochloric acid [1 part] and concentrated nitric acid [3 parts]
Concentrated hydrochloric acid [3 parts] and concentrated nitric acid [1 part]
Solutions for 8: Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-10-icse_6:654d3cd91177441db9833c3c89eccd66.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 8 (Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride are Hydrogen Chloride, Hydrochloric Acid, Uses of Hydrochloric Acid, General Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride Gas, Laboratory Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride Gas, Physical Properties of Hydrogen Chloride Gas, Chemical Properties of Hydrogen Chloride Gas, Laboratory Method of Preparation of Hydrochloric Acid, Properties of Hydrochloric Acid, Tests for Hydrogen Chloride and Hydrochloric Acid, Hydrogen Chloride, Hydrochloric Acid, Uses of Hydrochloric Acid, General Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride Gas, Laboratory Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride Gas, Physical Properties of Hydrogen Chloride Gas, Chemical Properties of Hydrogen Chloride Gas, Laboratory Method of Preparation of Hydrochloric Acid, Properties of Hydrochloric Acid, Tests for Hydrogen Chloride and Hydrochloric Acid.
Using Selina Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, Study of Compounds - Hydrogen Chloride Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
