Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A 60 kg man pushes a 40 kg man by a force of 60 N. The 40 kg man has pushed the other man with a force of
पर्याय
40 N
0 N
60 N
20 N
उत्तर
60 N
According to Newton's third law, which states that an action-reaction pair of forces are equal in magnitude, the man who weighs 40 kg will push the other man with the same force of 60 N.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
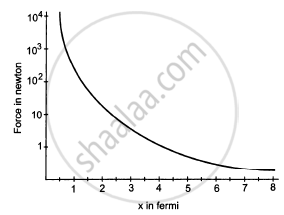
Suppose the magnitude of Nuclear force between two protons varies with the distance between them as shown in figure. Estimate the ratio "Nuclear force/Coulomb force" for
(a) x = 8 fm
(b) x = 4 fm
(c) x = 2 fm
(d) x = 1 fm (1 fm = 10 −15m).
When Neils Bohr shook hand with Werner Heisenberg, what kind of force they exerted ?
Let E, G and N represent the magnitudes of electromagnetic gravitational and nuclear forces between two electrons at a given separation. Then
The sum of all electromagnetic forces between different particles of a system of charged particles is zero
Calculate the force with which you attract the earth.
A monkey is sitting on a tree limb. The limb exerts a normal force of 48 N and a frictional force of 20 N. Find the magnitude of the total force exerted by the limb on the monkey.
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
A satellite is projected vertically upwards from an earth station. At what height above the earth's surface will the force on the satellite due to the earth be reduced to half its value at the earth station? (Radius of the earth is 6400 km.)
A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During the motion, the block is in
A box is pushed through 4.0 m across a floor offering 100 N resistance. How much work is done by the resisting force?
A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg in his hand. If he covers a distance of 40 m with an acceleration of 0⋅5 m/s2, find the work done by the man on the block during the motion.
A force \[F = \alpha + bx\] acts on a particle in the x-direction, where a and b are constants. Find the work done by this force during a displacement from x = 0 to x = d.
A block of mass 250 g slides down an incline of inclination 37° with uniform speed. Find the work done against friction as the block slides through 1m.
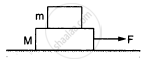
A block of mass m is kept over another block of mass M and the system rests on a horizontal surface (In the following figure). A constant horizontal force F acting on the lower block produces an acceleration \[\frac{F}{2 \left( m + M \right)}\] in the system, and the two blocks always move together. (a) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bigger block and the horizontal surface. (b) Find the frictional force acting on the smaller block. (c) Find the work done by the force of friction on the smaller block by the bigger block during a displacement d of the system.
A block of weight 100 N is slowly moved up a smooth incline of inclination 37° by a person. Calculate the work done by the person in moving the block through a distance of 2 m, if the driving force is (a) parallel to the incline and (b) in the horizontal direction.
A block of mass 1 kg is placed at point A of a rough track shown in figure following. If slightly pushed towards right, it stops at point B of the track. Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B.

A force F = 20 + 10y acts on a particle in y-direction where F is in newton and y in metre. Work done by this force to move the particle from y – 0 to y – 1 m is:
A bicyclist comes to a skidding stop in 10 m. During this process, the force on the bicycle due to the road is 200 N and is directly opposed to the motion. The work done by the cycle on the road is ______.
A block of mass 1 kg is pushed up a surface inclined to horizontal at an angle of 30° by a force of 10 N parallel to the inclined surface (Figure). The coefficient of friction between block and the incline is 0.1. If the block is pushed up by 10 m along the incline, calulate
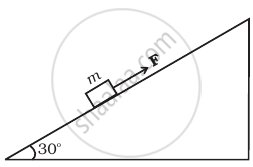
- work done against gravity
- work done against force of friction
- increase in potential energy
- increase in kinetic energy
- work done by applied force.
A body is displaced from (0, 0) to (1 m, 1 m) along the path x = y by a force F = (x2`hat"J"` + y`hat"i"`)N. The work done by this force will be:
