Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When Neils Bohr shook hand with Werner Heisenberg, what kind of force they exerted ?
पर्याय
Gravitational
Electromagnetic
Nuclear
Weak.
उत्तर
Electromagnetic
When Neils Bohr shook hand with Werner Heisenberg, electromagnetic force is exerted on each other. This is because when their hands made contact with each other, the atoms at the two surfaces come close to each other. The charged constituents of the atoms in the hands exert forces on each other and, as a result, a measurable force is produced.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
Work done in the motion of a body over a closed loop is zero for every force in nature.
A body of mass m is placed on a table. The earth is pulling the body with a force mg. Taking this force to be the action what is the reaction?
Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
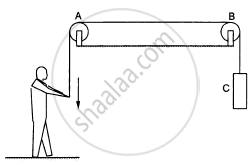
List all the forces acting on (a) the pulley A, (b) the boy and (c) the block C in figure.
The gravitational force acting on a particle of 1 g due to a similar particle is equal to 6.67 × 10−17 N. Calculate the separation between the particles.
Calculate the force with which you attract the earth.
At what distance should two charges, each equal to 1 C, be placed so that the force between them equals your weight ?
A monkey is sitting on a tree limb. The limb exerts a normal force of 48 N and a frictional force of 20 N. Find the magnitude of the total force exerted by the limb on the monkey.
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
Find the ratio of the magnitude of the electric force to the gravitational force acting between two protons.
A particle is acted upon by a force of constant magnitude which is always perpendicular to the velocity of the plane. The motion of the particle takes place in a plane. It follows that
(a) its velocity is constant
(b) its acceleration is constant
(c) its kinetic energy is constant
(d) it moves in a circular path.
A block of mass 5.0 kg slides down an incline of inclination 30° and length 10 m. Find the work done by the force of gravity.
A man moves on a straight horizontal road with a block of mass 2 kg in his hand. If he covers a distance of 40 m with an acceleration of 0⋅5 m/s2, find the work done by the man on the block during the motion.
Find the average frictional force needed to stop a car weighing 500 kg at a distance of 25 m if the initial speed is 72 km/h.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Show that the work done by the applied force does not exceed 40 J.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the work done by the force of gravity in that one second if the work done by the applied force is 40 J.
In a children's park, there is a slide which has a total length of 10 m and a height of 8⋅0 m . A vertical ladder is provided to reach the top. A boy weighing 200 N climbs up the ladder to the top of the slide and slides down to the ground. The average friction offered by the slide is three tenth of his weight. Find (a) the work done by the ladder on the boy as he goes up; (b) the work done by the slide on the boy as he comes down. Neglect any work done by forces inside the body of the boy
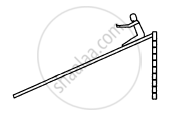
A block of mass 1 kg is placed at point A of a rough track shown in figure following. If slightly pushed towards right, it stops at point B of the track. Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B.

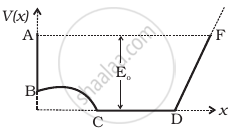
A graph of potential energy V(x) verses x is shown in figure. A particle of energy E0 is executing motion in it. Draw graph of velocity and kinetic energy versus x for one complete cycle AFA.
A block of mass 1 kg is pushed up a surface inclined to horizontal at an angle of 30° by a force of 10 N parallel to the inclined surface (Figure). The coefficient of friction between block and the incline is 0.1. If the block is pushed up by 10 m along the incline, calulate
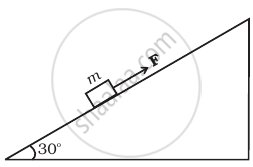
- work done against gravity
- work done against force of friction
- increase in potential energy
- increase in kinetic energy
- work done by applied force.
