Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A body is suspended from a spring balance kept in a satellite. The reading of the balance is W1 when the satellite goes in an orbit of radius R and is W2 when it goes in an orbit of radius 2 −R.
पर्याय
W1 = W2
W1 < W2
W1 > W2
W1 ≠ W2
उत्तर
W1 = W2
The gravitational pull on the satellite in both cases is used up in providing the necessary centripetal force required for its revolution around the earth. This means that there is no net force acting on the body which has been suspended from a spring balance in the satellite. So, the readings of the spring balance in both the cases are the same and is equal to zero.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens to the force between two objects, if the mass of one object is doubled?
Answer the following:
An astronaut inside a small space ship orbiting around the earth cannot detect gravity. If the space station orbiting around the earth has a large size, can he hope to detect gravity?
If you compare the gravitational force on the Earth due to the Sun to that due to the Moon, you would find that the Sun’s pull is greater than the Moon’s pull. (You can check this yourself using the data available in the succeeding exercises). However, the tidal effect of the Moon’s pull is greater than the tidal effect of Sun. Why?
Choose the correct answer from among the given ones:
For the problem 8.10, the direction of the gravitational intensity at an arbitrary point P is indicated by the arrow (i) d, (ii) e, (iii) f, (iv) g.
State and explain Kepler's laws of planetary motion. Draw diagrams to illustrate these laws.
Can two particles be in equilibrium under the action of their mutual gravitational force? Can three particles be? Can one of the three particles be?
At noon, the sun and the earth pull the objects on the earth's surface in opposite directions. At midnight, the sun and the earth pull these objects in same direction. Is the weight of an object, as measured by a spring balance on the earth's surface, more at midnight as compared to its weight at noon?
Four particles of equal masses M move along a circle of radius R under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction. Find the speed of each particle.
A semicircular wire has a length L and mass M. A particle of mass m is placed at the centre of the circle. Find the gravitational attraction on the particle due to the wire.
A solid sphere of mass m and radius r is placed inside a hollow thin spherical shell of mass M and radius R as shown in the following figure . A particle of mass m' is placed on the line joining the two centres at a distance x from the point of contact of the sphere and the shell. Find the magnitude of the resultant gravitational force on this particle due to the sphere and the shell if (a) r < x < 2r, (b) 2r < x < 2R and (c) x > 2R.
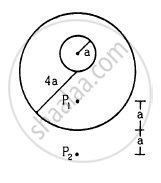
A uniform metal sphere of radius a and mass M is surrounded by a thin uniform spherical shell of equal mass and radius 4a (In the following figure). The centre of the shell falls on the surface of the inner sphere. Find the gravitational field at the points P1 and P2 shown in the figure.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It goes to a height 20 m and then returns to the ground. Taking acceleration due to gravity g to be 10 ms-2 , find :
the final velocity of the ball on reaching the ground .
A ball is thrown up with a speed of 4.9 ms-1.
Calculate the maximum height it would gain before it begins to fall.
At what height above the earth's surface would the value of acceleration due to gravity be half of what it is on the surface? Take the radius of earth to be R.
A force can produce ________, In an object at rest. It can __________ an object and change its __________ of motion.
An apple falls towards the earth due to its gravitational force. The apple also attracts the earth with the same force. Why do we not see the earth rising towards the apple? Explain.
Particles of masses 2M, m and M are respectively at points A, B and C with AB = ½ (BC). m is much-much smaller than M and at time t = 0, they are all at rest (Figure). At subsequent times before any collision takes place ______.

Give scientific reasons for the following:
Newton's gravitational law is the universal law of gravitation.
Write the answer of the question with reference to laws of gravitation.
Write the value of the universal gravitational constant.
Observe the figure and answer the questions:
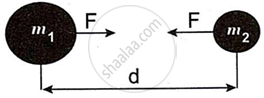
- State Newton's universal law of gravitation.
- If the distance between the two bodies is tripled, how will the gravitational force between them change?
- What will happen to gravitational force, if mass of one of the object is doubled?
