Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A bullet of mass 25 g is fired horizontally into a ballistic pendulum of mass 5.0 kg and gets embedded in it. If the centre of the pendulum rises by a distance of 10 cm, find the speed of the bullet.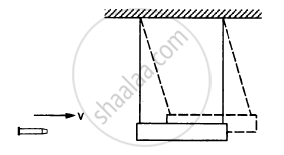
उत्तर
Given:
Mass of bullet, m = 25 g = 0.025 kg
Mass of ballistic pendulum, M = 5 kg
Vertical displacement, h = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Let the bullet strikes the pendulum with a velocity u.
Let the final velocity be v.
Using the law of conservation of linear momentum, we can write:
\[mu = (M + m)v\]
\[ \Rightarrow v = \frac{m}{(M + m)}u\]
\[ \Rightarrow v = \frac{0 . 25}{5 . 025} \times u = \frac{u}{201}\]
Applying the law of conservation of energy, we get:
\[\left( \frac{1}{2} \right)(M + m) v^2 = (M + m)gh\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{u^2}{(201 )^2} = 2 \times 10 \times 0 . 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow u = 201 \times \sqrt{2} = 280 \text{ m/s}\]
The bullet strikes the pendulum with a velocity of 280 m/s.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two bodies make an elastic head-on collision on a smooth horizontal table kept in a car. Do you expect a change in the result if the car is accelerated in a horizontal road because of the non inertial character of the frame? Does the equation "Velocity of separation = Velocity of approach" remain valid in an accelerating car? Does the equation "final momentum = initial momentum" remain valid in the accelerating car?
If the linear momentum of a particle is known, can you find its kinetic energy? If the kinetic energy of a particle is know can you find its linear momentum?
Suppose we define a quantity 'Linear momentum' as linear momentum = mass × speed.
The linear momentum of a system of particles is the sum of linear momenta of the individual particles. Can we state principle of conservation of linear momentum as "linear momentum of a system remains constant if no external force acts on it"?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Take "the table plus the ball" as the system. friction between the table and the ball is then an internal force. As the ball slows down, the momentum of the system decreases. Which external force is responsible for this change in the momentum?
A shell is fired from a cannon with a velocity V at an angle θ with the horizontal direction. At the highest point in its path, it explodes into two pieces of equal masses. One of the pieces retraces its path to the cannon. The speed of the other piece immediately after the explosion is
A ball hits a floor and rebounds after an inelastic collision. In this case
(a) the momentum of the ball just after the collision is same as that just before the collision
(b) the mechanical energy of the ball remains the same during the collision
(c) the total momentum of the ball and the earth is conserved
(d) the total energy of the ball and the earth remains the same
A uranium-238 nucleus, initially at rest, emits an alpha particle with a speed of 1.4 × 107m/s. Calculate the recoil speed of the residual nucleus thorium-234. Assume that the mass of a nucleus is proportional to the mass number.
A man of mass 50 kg starts moving on the earth and acquires a speed 1.8 m/s. With what speed does the earth recoil? Mass of earth = 6 × 1024 kg.
A man of mass M having a bag of mass m slips from the roof of a tall building of height H and starts falling vertically in the following figure. When at a height h from the ground, the notices that the ground below him is pretty hard, but there is a pond at a horizontal distance x from the line of fall. In order to save himself he throws the bag horizontally (with respect to himself) in the direction opposite to the pond. Calculate the minimum horizontal velocity imparted to the bag so that the man lands in the water. If the man just succeeds to avoid the hard ground, where will the bag land?
A ball of mass 0.50 kg moving at a speed of 5.0 m/s collides with another ball of mass 1.0 kg. After the collision the balls stick together and remain motionless. What was the velocity of the 1.0 kg block before the collision?
In a gamma decay process, the internal energy of a nucleus of mass M decreases, a gamma photon of energy E and linear momentum E/c is emitted and the nucleus recoils. Find the decrease in internal energy.
A block of mass 200 g is suspended through a vertical spring. The spring is stretched by 1.0 cm when the block is in equilibrium. A particle of mass 120 g is dropped on the block from a height of 45 cm. The particle sticks to the block after the impact. Find the maximum extension of the spring. Take g = 10 m/s2.
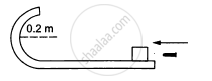
A bullet of mass 10 g moving horizontally at a speed of 50√7 m/s strikes a block of mass 490 g kept on a frictionless track as shown in figure. The bullet remains inside the block and the system proceeds towards the semicircular track of radius 0.2 m. Where will the block strike the horizontal part after leaving the semicircular track?
Suppose the particle of the previous problem has a mass m and a speed \[\nu\] before the collision and it sticks to the rod after the collision. The rod has a mass M. (a) Find the velocity of the centre of mass C of the system constituting "the rod plus the particle". (b) Find the velocity of the particle with respect to C before the collision. (c) Find the velocity of the rod with respect to C before the collision. (d) Find the angular momentum of the particle and of the rod about the centre of mass C before the collision. (e) Find the moment of inertia of the system about the vertical axis through the centre of mass C after the collision. (f) Find the velocity of the centre of mass C and the angular velocity of the system about the centre of mass after the collision.
A small disc is set rolling with a speed \[\nu\] on the horizontal part of the track of the previous problem from right to left. To what height will it climb up the curved part?
A solid sphere of mass m is released from rest from the rim of a hemispherical cup so that it rolls along the surface. If the rim of the hemisphere is kept horizontal, find the normal force exerted by the cup on the ball when the ball reaches the bottom of the cup.
The following figure shows a small spherical ball of mass m rolling down the loop track. The ball is released on the linear portion at a vertical height H from the lowest point. The circular part shown has a radius R.
(a) Find the kinetic energy of the ball when it is at a point A where the radius makes an angle θ with the horizontal.
(b) Find the radial and the tangential accelerations of the centre when the ball is at A.
(c) Find the normal force and the frictional force acting on the if ball if H = 60 cm, R = 10 cm, θ = 0 and m = 70 g.

