Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A bullet of mass 20 g moving horizontally at a speed of 300 m/s is fired into a wooden block of mass 500 g suspended by a long string. The bullet crosses the block and emerges on the other side. If the centre of mass of the block rises through a height of 20.0 cm, find the speed of the bullet as it emerges from the block.
उत्तर
Given:
Mass of bullet, m = 20 gm = 0.02 kg
Horizontal speed of the bullet, u = 300 m/s
Mass of wooden block, M = 500 gm = 0.5 kg
Let the bullet emerges out with velocity v.
Let the velocity of the block be v'.
Using the law of conservation of momentum, we get:
mu = Mv' + mv ...(1)
Now, applying the work-energy principle for the block after the collision, we get:
\[0 - \left( \frac{1}{2} \right)M \times \left( v' \right)^2 = - Mgh\]
\[ \Rightarrow (v' )^2 = 2gh\]
\[ v' = \sqrt{2gh}\]
\[ = \sqrt{20 \times 10 \times 0 . 2} = 2 \text{ m/s}\]
On substituting the value of v' in equation (1), we get:
\[0 . 02 \times 300 = 0 . 5 \times 2 + 0 . 02 \times v\]
\[ \Rightarrow v = \frac{6 - 1}{0 . 02} = \frac{5}{0 . 02}\]
\[ \Rightarrow v = 250 \text{ m/s}\]
\[0 . 02 \times 300 = 0 . 5 \times 2 + 0 . 02 \times v\]
\[ \Rightarrow v = \frac{6 - 1}{0 . 02} = \frac{5}{0 . 02}\]
\[ \Rightarrow v = 250 \text{ m/s}\]
Hence, the speed of the bullet as it emerges out from the block is 250 m/s.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the linear momentum of a particle is known, can you find its kinetic energy? If the kinetic energy of a particle is know can you find its linear momentum?
Use the definition of linear momentum from the previous question. Can we state the principle of conservation of linear momentum for a single particle?
A van is standing on a frictionless portion of a horizontal road. To start the engine, the vehicle must be set in motion in the forward direction. How can be persons sitting inside the van do it without coming out and pushing from behind?
A bullet hits a block kept at rest on a smooth horizontal surface and gets embedded into it. Which of the following does not change?
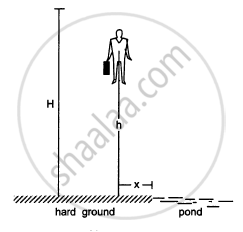
A man of mass M having a bag of mass m slips from the roof of a tall building of height H and starts falling vertically in the following figure. When at a height h from the ground, the notices that the ground below him is pretty hard, but there is a pond at a horizontal distance x from the line of fall. In order to save himself he throws the bag horizontally (with respect to himself) in the direction opposite to the pond. Calculate the minimum horizontal velocity imparted to the bag so that the man lands in the water. If the man just succeeds to avoid the hard ground, where will the bag land?
A ball of mass 50 g moving at a speed of 2.0 m/s strikes a plane surface at an angle of incidence 45°. The ball is reflected by the plane at equal angle of reflection with the same speed. Calculate (a) the magnitude of the change in momentum of the ball (b) the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball.
A ball of mass 0.50 kg moving at a speed of 5.0 m/s collides with another ball of mass 1.0 kg. After the collision the balls stick together and remain motionless. What was the velocity of the 1.0 kg block before the collision?
A ball of mass m moving at a speed v makes a head-on collision with an identical ball at rest. The kinetic energy of the balls after the collision is three fourths of the original. Find the coefficient of restitution.
A block of mass 2.0 kg is moving on a frictionless horizontal surface with a velocity of 1.0 m/s (In the following figure) towards another block of equal mass kept at rest. The spring constant of the spring fixed at one end is 100 N/m. Find the maximum compression of the spring.

A bullet of mass 20 g travelling horizontally with a speed of 500 m/s passes through a wooden block of mass 10.0 kg initially at rest on a level surface. The bullet emerges with a speed of 100 m/s and the block slides 20 cm on the surface before coming to rest. Find the friction coefficient between the block and the surface (See figure).
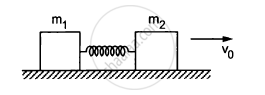
Two blocks of masses m1 and m2 are connected by a spring of spring constant k (See figure). The block of mass m2 is given a sharp impulse so that it acquires a velocity v0 towards right. Find (a) the velocity of the centre of mass, (b) the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer.
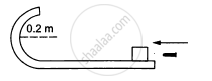
A bullet of mass 10 g moving horizontally at a speed of 50√7 m/s strikes a block of mass 490 g kept on a frictionless track as shown in figure. The bullet remains inside the block and the system proceeds towards the semicircular track of radius 0.2 m. Where will the block strike the horizontal part after leaving the semicircular track?
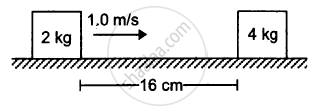
The friction coefficient between the horizontal surface and each of the block shown in figure is 0.20. The collision between the blocks is perfectly elastic. Find the separation between the two blocks when they come to rest. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A uniform rod pivoted at its upper end hangs vertically. It is displaced through an angle of 60° and then released. Find the magnitude of the force acting on a particle of mass dm at the tip of the rod when the rod makes an angle of 37° with the vertical.
A small disc is set rolling with a speed \[\nu\] on the horizontal part of the track of the previous problem from right to left. To what height will it climb up the curved part?
The following figure shows a small spherical ball of mass m rolling down the loop track. The ball is released on the linear portion at a vertical height H from the lowest point. The circular part shown has a radius R.
(a) Find the kinetic energy of the ball when it is at a point A where the radius makes an angle θ with the horizontal.
(b) Find the radial and the tangential accelerations of the centre when the ball is at A.
(c) Find the normal force and the frictional force acting on the if ball if H = 60 cm, R = 10 cm, θ = 0 and m = 70 g.

The track shown is figure is frictionless. The block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A or mass m is pushed along the track with some speed. The collision between Aand B is perfectly elastic. With what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened?

