Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A man fixes outside his house one evening a two metre high insulating slab carrying on its top a large aluminium sheet of area 1 m2. Will he get an electric shock if he touches the metal sheet next morning?
उत्तर
Yes, the man will get an electric shock if he touches the metal slab next morning. The steady discharging current in the atmosphere charges up the aluminium sheet. As a result, its voltage rises gradually. The rise in the voltage depends on the capacitance of the capacitor formed by the aluminium slab and the ground.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Describe schematically the equipotential surfaces corresponding to
(a) a constant electric field in the z-direction,
(b) a field that uniformly increases in magnitude but remains in a constant (say, z) direction,
(c) a single positive charge at the origin, and
(d) a uniform grid consisting of long equally spaced parallel charged wires in a plane.
The discharging current in the atmosphere due to the small conductivity of air is known to be 1800 A on an average over the globe. Why then does the atmosphere not discharge itself completely in due course and become electrically neutral? In other words, what keeps the atmosphere charged?
What are the forms of energy into which the electrical energy of the atmosphere is dissipated during a lightning?
(Hint: The earth has an electric field of about 100 Vm−1 at its surface in the downward direction, corresponding to a surface charge density = −10−9 C m−2. Due to the slight conductivity of the atmosphere up to about 50 km (beyond which it is good conductor), about + 1800 C is pumped every second into the earth as a whole. The earth, however, does not get discharged since thunderstorms and lightning occurring continually all over the globe pump an equal amount of negative charge on the earth.)
Draw the equipotential surfaces due to an electric dipole. Locate the points where the potential due to the dipole is zero.
Answer the following question.
Two identical point charges, q each, are kept 2m apart in the air. A third point charge Q of unknown magnitude and sign is placed on the line joining the charges such that the system remains in equilibrium. Find the position and nature of Q.
Depict the equipotential surface due to
(i) an electric dipole,
(ii) two identical positive charges separated by a distance.
A particle of mass 'm' having charge 'q' is held at rest in uniform electric field of intensity 'E'. When it is released, the kinetic energy attained by it after covering a distance 'y' will be ______.
Equipotentials at a great distance from a collection of charges whose total sum is not zero are approximately.
- The potential at all the points on an equipotential surface is same.
- Equipotential surfaces never intersect each other.
- Work done in moving a charge from one point to other on an equipotential surface is zero.
Equipotential surfaces ______.
Can two equipotential surfaces intersect each other?
The work done to move a charge along an equipotential from A to B ______.
- cannot be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- must be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- is zero.
- can have a non-zero value.
Prove that a closed equipotential surface with no charge within itself must enclose an equipotential volume.
Draw equipotential surfaces for (i) an electric dipole and (ii) two identical positive charges placed near each other.
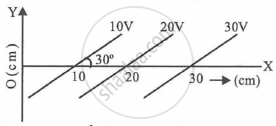
Equipotential surfaces are shown in figure. Then the electric field strength will be ______.