Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A population will not exist in Hardly Weiberg equilibrium if ____________.
पर्याय
Individuals mate selectively
There are no mutations
There is no migration
The population is large
उत्तर
A population will not exist in Hardly Weiberg equilibrium if Individuals mate selectively.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the graphical representation of Hardy· Weinberg's principle in the form of Punnet Square.
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1. Explain this algebraic equation on the basis of Hardy Weinberg's principle.
With the help of an algebraic equation, how did Hardy-Weinberg explain that in a given population the frequency of occurrence of alleles of a gene is supposed to remain the same through generations?
Differentiate between Directional natural selection and Disruptive natural selection.
What is the Founder's effect?
According to the Hardy-Weinberg principle, the allele frequency of a population remains constant. How do you interpret the change of frequency of alleles in a population?
Multiple choice question.
In Hardy - Weinberg equation, the frequency of homozygous recessive individual is represented by:
How does Hardy-Weinberg’s expression (p2+2pq+q2=1) explain that genetic equilibrium is maintained in a population? List any four factors that can disturb the genetic equilibrium.
Hardy - Weinberg equilibrium is known to be affected by gene - flow, genetic drift, mutation, genetic recombination and
Disturbance of Hardy - Weinberg equilibrium results in
Gene flow occurs through generations. and can occur across language barriers in humans. If we have a technique of measuring specific allele frequencies in different population of the world, can we not predict human migratory patterns in pre-history and history? Do you agree or disagree? Provide explanation to your answer.
How is Hardy-Weinberg's expression “(p2 + 2pq + q2) = 1” derived?
The graphs below show three types of natural selection. The shaded areas marked with arrows show the individuals in the population who are not selected. The dotted vertical lines show the statistical means.
 |
 |
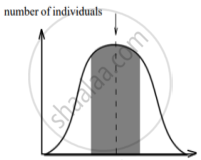 |
| character Graph A |
character Graph B |
character Graph C |
- What names are given to the types of selection shown in graphs A, B and C?
- After the selection has operated for several generations in the above populations indicated as, Graph A, B and C, graphically illustrate the probable results.
Write Hardy Weinberg's equation.
Give a mathematical expression for Hardy Weinberg's principle.
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
Frequency of the allele (A).
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
The number of carrier fruit flies.
The black colour on the beak of finches dominates over the yellow colour. There are 210 individuals with the genotype DD, 245 individuals with the genotype Dd and 45 individuals with the genotype dd. Deduce the frequency of individuals with dominant, heterozygous, and recessive traits.
