Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A simple pendulum consists of a small sphere of mass m suspended by a thread of length l. The sphere carries a positive charge q. The pendulum is placed in a uniform electric field of strength E directed vertically downwards. Find the period of oscillation of the pendulum due to the electrostatic force acting on the sphere, neglecting the effect of the gravitational force.
उत्तर
The length of the thread = l
Mass of the sphere = m
Charge on the sphere = +q
Force on sphere due to a downward electric field = qE (downward)
As the gravitational force is neglected hence net force on the conductor is the force due to the electric field. i.e.
Fnet = qE
So-net acceleration = `"qE"/"m"`
Hence the time period of the pendulum is `"T" = 2pi sqrt("l"/(("qE"/"m"))) = 2pi sqrt("ml"/"qE")`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) If two similar large plates, each of area A having surface charge densities +σ and –σ are separated by a distance d in air, find the expressions for
(a) field at points between the two plates and on outer side of the plates. Specify the direction of the field in each case.
(b) the potential difference between the plates.
(c) the capacitance of the capacitor so formed.
(ii) Two metallic spheres of Radii R and 2R are charged so that both of these have same surface charge density σ. If they are connected to each other with a conducting wire, inn which direction will the charge flow and why?
plot a graph showing the variation of current density (j) versus the electric field (E) for two conductors of different materials. What information from this plot regarding the properties of the conducting material, can be obtained which can be used to select suitable materials for use in making (i) standard resistance and (ii) connecting wires in electric circuits?
Two identical circular loops 1 and 2 of radius R each have linear charge densities −λ and +λ C/m respectively. The loops are placed coaxially with their centres `Rsqrt3` distance apart. Find the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at the centre of loop 1.
The radius of a gold nucleus (Z = 79) is about 7.0 × 10-10 m. Assume that the positive charge is distributed uniformly throughout the nuclear volume. Find the strength of the electric field at (a) the surface of the nucleus and (b) at the middle point of a radius. Remembering that gold is a conductor, is it justified to assume that the positive charge is uniformly distributed over the entire volume of the nucleus and does not come to the outer surface?
A non-conducting sheet of large surface area and thickness d contains a uniform charge distribution of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the plate, at a distance x from the central plane. Draw a qualitative graph of E against x for 0 < x < d.
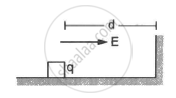
A block of mass containing a net positive charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table which terminates in a vertical wall as shown in the figure. The distance of the block from the wall is d. A horizontal electric field E towards the right is switched on. Assuming elastic collisions (if any), find the time period of the resulting oscillatory motion. Is it a simple harmonic motion?
Answer the following question.
Prove that the average energy density of the oscillating electric field is equal to that of the oscillating magnetic field.
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
