Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
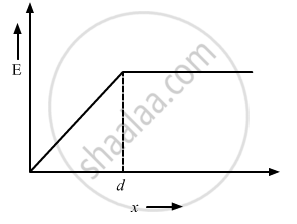
A non-conducting sheet of large surface area and thickness d contains a uniform charge distribution of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the plate, at a distance x from the central plane. Draw a qualitative graph of E against x for 0 < x < d.
उत्तर
Given:
Thickness of the sheet = d
Let the surface area of the sheet be s.
Volume of the sheet = sd
Volume charge density of the sheet, ρ = `"Q"/"sd"`
Charge on the sheet = Q

Consider an imaginary plane at a distance x from the central plane of surface area s.
Charge enclosed by this sheet, q =ρsx
For this Guassian surface, using Gauss's Law,we get:
`oint "E"."ds" = "q"/∈_0`
`"E"."s" = (ρ "sx")/∈_0`
`"E" =( ρ "x")/∈_0`
The electric field outside the sheet will be constant and will be:
`"E" =(ρ"d")/∈_0 `
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Plot a graph showing the variation of resistivity of a conductor with temperature.
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
A metallic particle with no net charge is placed near a finite metal plate carrying a positive charge. The electric force on the particle will be
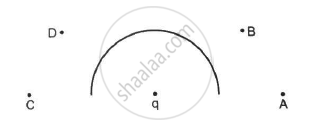
In the following figure shows a charge q placed at the centre of a hemisphere. A second charge Q is placed at one of the positions A, B, C and D. In which position(s) of this second charge, the flux of the electric field through the hemisphere remains unchanged?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Show that there can be no net charge in a region in which the electric field is uniform at all points.
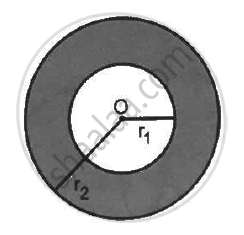
A charge Q is distributed uniformly within the material of a hollow sphere of inner and outer radii r1 and r2 (see the figure). Find the electric field at a point P at a distance x away from the centre for r1 < x < r. Draw a rough graph showing the electric field as a function of x for 0 < x < 2r2 (see the figure).
A charged particle with a charge of −2⋅0 × 10−6 C is placed close to a non-conducting plate with a surface charge density of 4.0 × 10-6Cm0-2. Find the force of attraction between the particle and the plate.
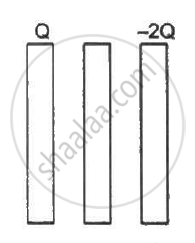
Three identical metal plates with large surface areas are kept parallel to each other as shown in the following figure. The leftmost plate is given a charge Q, the rightmost a charge −2Q and the middle one is kept neutral. Find the charge appearing on the outer surface of the rightmost plate.
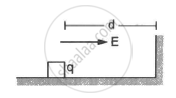
A block of mass containing a net positive charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table which terminates in a vertical wall as shown in the figure. The distance of the block from the wall is d. A horizontal electric field E towards the right is switched on. Assuming elastic collisions (if any), find the time period of the resulting oscillatory motion. Is it a simple harmonic motion?
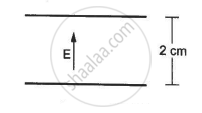
An electric field of magnitude 1000 NC−1 is produced between two parallel plates with a separation of 2.0 cm, as shown in the figure. (a) What is the potential difference between the plates? (b) With what minimum speed should an electron be projected from the lower place in the direction of the field, so that it may reach the upper plate? (c) Suppose the electron is projected from the lower place with the speed calculated in part (b). The direction of projection makes an angle of 60° with the field. Find the maximum height reached by the electron.
A uniform field of 2.0 NC−1 exists in space in the x-direction. (a) Taking the potential at the origin to be zero, write an expression for the potential at a general point (x, y, z). (b) At which point, the potential is 25 V? (c) If the potential at the origin is taken to be 100 V, what will be the expression for the potential at a general point? (d) What will be the potential at the origin if the potential at infinity is taken to be zero? Is it practical to choose the potential at infinity to be zero?
Draw equipotential surfaces corresponding to a uniform electric field in the z-directions.
Answer the following question.
Prove that the average energy density of the oscillating electric field is equal to that of the oscillating magnetic field.
The force per unit charge is known as ______.
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
Two charged conducting spheres of radii a and b are connected to each other by a wire. Find the ratio of the electric fields at their surfaces.
