Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A six sided die is marked ‘1’ on one face, ‘3’ on two of its faces, and ‘5’ on remaining three faces. The die is thrown twice. If X denotes the total score in two throws, find the cumulative distribution function
उत्तर
Let X be the random variable denotes the total score in two thrown of a die.
Sample space S
| I\II | 1 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 3 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 3 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| 5 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 5 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 5 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
n(S) = 36
X = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}
| Values of the random variable | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | Total |
| Number of elements in inverse image | 1 | 4 | 10 | 12 | 9 | 36 |
Cumulative distribution function
F(x) = P(X ≤ x)
= `sum_(x_"i" ≤ x) "P"("X" = x_"i")`
F(2) = P(X < 2)
= P(X < 2) + P(X = 2)
= `0 + 1/36`
= `1/36`
F(4) = `"P"("X" ≤ 4)`
= P(X <2) + P(X = 2) + P(X = 4)
= `0+ 1/36 + 4/36`
= `5/36`
F(6) = `"P"("X" ≤ 6)`
= P(X < 2) + P(X = 2) + P(X = 4) + P(X = 6)
= `0 + 11/36+ 4/36 + 10/36`
= `15/36`
F(8) = P(X ≤ 8)
= P(X < 2) + P(X = 2) + P(X = 4) + P(X = 6) + P(X = 8)
= `0 + 1/6 + 4/36 + 10/36 + 12/36`
= `27/36`
F(10) = P(X ≤ 10)
= P(X < 2) + P(X = 2) + P(x = 8) + P(X = 10)
= `0 + 1/36 + 4/36 + 10/36 + 12/36 + 9/36`
= `36/36`
= 1
F(x) = `{{:(0",", "For" - oo < x < 2),(1/36",", "For" 2 ≤ x ≤ 4),(5/36",", "For" 4 ≤ x < 6),(15/36",", "For" 6 ≤ x < 8),(27/36",", "For" 8 ≤ x < 10),(1",", "For" 10 ≤ x < oo):}`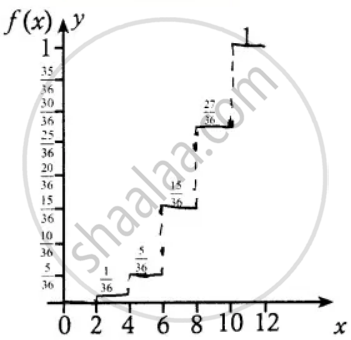
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given the p.d.f. of a continuous r.v. X , f (x) = `x^2/3` ,for –1 < x < 2 and = 0 otherwise
Determine c.d.f. of X hence find
P( x < 1)
Given the p.d.f. of a continuous r.v. X ,
f (x) = `x^2/3` , for –1 < x < 2 and = 0 otherwise
Determine c.d.f. of X hence find P(1 < x < 2)
It is felt that error in measurement of reaction temperature (in celsius) in an experiment is a continuous r.v. with p.d.f.
f(x) = `{(x^3/(64), "for" 0 ≤ x ≤ 4),(0, "otherwise."):}`
Verify whether f(x) is a p.d.f.
Solve the following problem :
Identify the random variable as discrete or continuous in each of the following. Identify its range if it is discrete.
Twelve of 20 white rats available for an experiment are male. A scientist randomly selects 5 rats and counts the number of female rats among them.
c.d.f. of a discrete random variable X is
Find the probability mass function and cumulative distribution function of a number of girl children in families with 4 children, assuming equal probabilities for boys and girls
Suppose a discrete random variable can only take the values 0, 1, and 2. The probability mass function is defined by
`f(x) = {{:((x^2 + 1)/k"," "for" x = 0"," 1"," 2),(0"," "otherwise"):}`
Find P(X ≥ 1)
A random variable X has the following probability mass function.
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| F(x) | k2 | 2k2 | 3k2 | 2k | 3k |
Find the value of k
The cumulative distribution function of a discrete random variable is given by
F(x) = `{{:(0, "for" - oo < x < 0),(1/2, "for" 0 ≤ x < 1),(3/5, "for" 1 ≤ x < 2),(4/5, "for" 2 ≤ x < 4),(9/5, "for" 3 ≤ x < 4),(1, "for" ≤ x < oo):}`
Find P(X ≥ 2)
If Xis a.r.v. with c.d.f F (x) and its probability distribution is given by
| X = x | - 1.5 | -0.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 |
| P(X = x) | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.35 |
then, F(1.5) - F(- 0.5) = ?
Choose the correct alternative:
Suppose that X takes on one of the values 0, 1 and 2. If for some constant k, P(X = i) = kP(X = i – 1) for i = 1, 2 and P(X = 0) = `1/7`. Then the value of k is
Let X = time (in minutes) that lapses between the ringing of the bell at the end of a lecture and the actual time when the professor ends the lecture. Suppose X has p.d.f.
f(x) = `{(kx^2"," 0 ≤ x ≤ 2), (0"," "othenwise"):}`
Then, the probability that the lecture ends within 1 minute of the bell ringing is ______
If the probability function of a random variable X is defined by P(X = k) = a`((k + 1)/2^k)` for k - 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, then the probability that X takes a prime value is ______
X is a continuous random variable with a probability density function
f(x) = `{{:(x^2/4 + k; 0 ≤ x ≤ 2),(0; "otherwise"):}`
The value of k is equal to ______
The probability distribution of a random variable X is given below.
| X = k | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X = k) | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0 |
The variance of X is ______
Two coins are tossed. Then the probability distribution of number of tails is.
The c.d.f. of a discrete r.v. X is
| X = x | -4 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
| F(x) | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 0.75 | 0.80 | 0.95 | 1 |
Then P(X ≤ 4|X > -1) = ?
A random variable X has the following probability distribution:
| X = xi | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| P(X = xi) | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 0.35 |
The mean and the variance are respectively ______.
A coin is tossed three times. If X denotes the absolute difference between the number of heads and the number of tails then P(X = 1) = ______.
