Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A solution of \[\ce{Ni(NO3)2}\] is electrolysed between platinum electrodes using a current of 5 amperes for 20 minutes. What mass of \[\ce{Ni}\] is deposited at the cathode?
उत्तर
The reaction takes place in the following manner-
\[\ce{Ni^{2+} + 2e^- -> Ni}\]
Atomic weight of \[\ce{Ni}\] = 58.70
Equivalent weight of \[\ce{Ni}\] = `("atomic weight")/("number of valence electrons")`
= `58.70/2`
= 29.35
According to Faraday's first law of electrolysis,
W = `"Z"."I"."t" = "Equivalent weight"/96500 xx "I" xx "t"`
= `29.35/96500 xx 5 xx 20 xx 60`
= 1.825 g
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
On calculating the strength of current in amperes if a charge of 840C (coulomb) passes through an electrolyte in 7 minutes, it will be
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
The charge of how many coulomb is required to deposit 1.0 g of sodium metal (molar mass 23.0 g mol-1) from sodium ions is -
- 2098
- 96500
- 193000
- 4196
96500 coulombs correspond to the charge on how many electrons?
State the first law of electrolysis
Consider the reaction: \[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}_7 + 14H^+ + 6e^- -> 2Cr^{3+} + 7H2O}\]
What is the quantity of electricity in coulombs needed to reduce 1 mol of \[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}_7}\]?
How much charge is required for the following reduction:
1 mol of \[\ce{MnO^-_4}\] to \[\ce{Mn^{2+}}\]?
Three electrolytic cells A, B, C containing solutions of \[\ce{ZnSO4}\], \[\ce{AgNO3}\] and \[\ce{CuSO4}\], respectively, are connected in series. A steady current of 1.5 amperes was passed through them until 1.45 g of silver deposited at the cathode of cell B. How long did the current flow? What mass of copper and zinc were deposited?
On passing 1.5 F charge, the number of moles of aluminium deposited at cathode are _______ [Molar mass of Al = 27 gram mol–1]
(A) 1.0
(B) 13.5
(C) 0.50
(D) 0.75
Draw neat labelled diagram of electrolytic refining of blister copper
Following reactions occur at cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous copper(II) chloride solution :
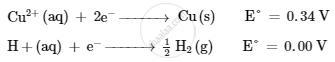
On the basis of their standard reduction electrode potential (E°) values, which reaction is feasible at the cathode and why ?
Solve the following question.
A steady current of 2 amperes was passed through two electrolytic cells X and Y connected in series containing electrolytes FeSO4 and ZnSO4 until 2.8 g of Fe deposited at the cathode of cell X. How long did the current flow? Calculate the mass of Zn deposited at the cathode of cell Y.
(Molar mass : Fe = 56 g mol–1, Zn = 65.3 g mol–1, 1F = 96500 C mol–1)
According to Faraday’s First Law of Electrolysis, the amount of chemical reaction which occurs at any electrode during electrolysis by a current is proportional to the ____________.
In the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride solution which of the half cell reaction will occur at anode?
Assertion: Electrolysis of NaCl solution gives chlorine at anode instead of O2.
Reason: Formation of oxygen at anode requires overvoltage.
When during electrolysis of a solution of Ag No3, 9650 coulombs of charge pass through the electroplating bath, the mass of silver deposite on the cathode will be:-
The quantity of electricity needed to separately electrolyse 1 M solution of ZnSO4, AlCl3, and AgNO3 completely is in the ratio of ______.
A current of 4 amp was passed for 2 hours through a solution of copper sulphate when 5.0 g of copper was deposited. The current efficiency is ______% (Cu = 63.5).
Assertion (A): During electrolysis of aqueous copper sulphate solution using copper electrodes hydrogen gas is released at the cathode.
Reason (R): The electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu is greater than that of H+/H2.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
