Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A steel blade placed gently on the surface of water floats on it. If the same blade is kept well inside the water, it sinks. Explain.
उत्तर
It floats because of the surface tension of water. The surface of water behaves like a stretched membrane. When a blade is placed on the water surface, it's unable to pierce the stretched membrane of water due to its low weight and remains floating.
However, if the blade is placed below the surface of water, it no longer experiences the surface tension and sinks to the bottom as the density of the blade is greater than that of water.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Determine the volume contraction of a solid copper cube, 10 cm on an edge, when subjected to a hydraulic pressure of 7.0 ×106 Pa.
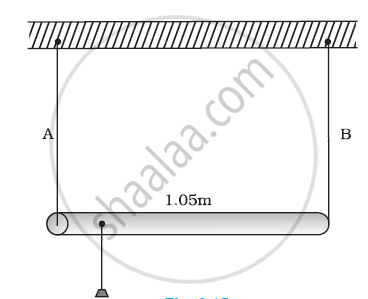
A rod of length 1.05 m having negligible mass is supported at its ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths as shown in Figure. The cross-sectional areas of wires A and B are 1.0 mm2 and 2.0 mm2, respectively. At what point along the rod should a mass m be suspended in order to produce (a) equal stresses and (b) equal strains in both steel and aluminium wires.
Two strips of metal are riveted together at their ends by four rivets, each of diameter 6.0 mm. What is the maximum tension that can be exerted by the riveted strip if the shearing stress on the rivet is not to exceed 6.9 × 107 Pa? Assume that each rivet is to carry one-quarter of the load.
When the skeleton of an elephant and the skeleton of a mouse are prepared in the same size, the bones of the elephant are shown thicker than those of the mouse. Explain why the bones of an elephant are thicker than proportionate. The bones are expected to withstand the stress due to the weight of the animal.
When some wax is rubbed on a cloth, it becomes waterproof. Explain.
A heave uniform rod is hanging vertically form a fixed support. It is stretched by its won weight. The diameter of the rod is
Answer in one sentence.
How should be a force applied on a body to produce shearing stress?
A charged particle is moving in a uniform magnetic field in a circular path of radius R. When the energy of the particle becomes three times the original, the new radius will be ______.
A rod has a radius of 100 mm and a length of 10 cm. A 100 N force compress along its length. Calculate the longitudinal stress developed in the rod.
Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is ______.
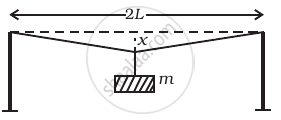
A mild steel wire of length 2L and cross-sectional area A is stretched, well within elastic limit, horizontally between two pillars (Figure). A mass m is suspended from the mid point of the wire. Strain in the wire is ______.
A rectangular frame is to be suspended symmetrically by two strings of equal length on two supports (Figure). It can be done in one of the following three ways;
| (a) |  |
| (b) |  |
| (c) |  |
The tension in the strings will be ______.
Consider two cylindrical rods of identical dimensions, one of rubber and the other of steel. Both the rods are fixed rigidly at one end to the roof. A mass M is attached to each of the free ends at the centre of the rods.
A wire is suspended from the ceiling and stretched under the action of a weight F suspended from its other end. The force exerted by the ceiling on it is equal and opposite to the weight.
- Tensile stress at any cross section A of the wire is F/A.
- Tensile stress at any cross section is zero.
- Tensile stress at any cross section A of the wire is 2F/A.
- Tension at any cross section A of the wire is F.
A rod of length l and negligible mass is suspended at its two ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths (Figure). The cross-sectional areas of wires A and B are 1.0 mm2 and 2.0 mm2, respectively.
(YAl = 70 × 109 Nm−2 and Ysteel = 200 × 109 Nm–2)
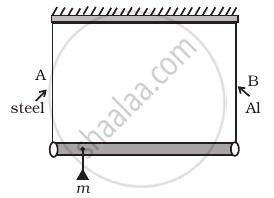
- Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have equal stresses in both the wires.
- Mass m should be suspended close to B to have equal stresses in both the wires.
- Mass m should be suspended at the middle of the wires to have equal stresses in both the wires.
- Mass m should be suspended close to wire A to have equal strain in both wires.
If 'S' is stress and 'Y' is young's modulus of the material of a wire, the energy stored in the wire per unit volume is ______.
A body of mass m = 10 kg is attached to one end of a wire of length 0.3 m. The maximum angular speed (in rad s-1) with which it can be rotated about its other end in the space station is (Breaking stress of wire = 4.8 × 107 Nm-2 and the area of cross-section of the wire = 10-2 cm2) is ______.
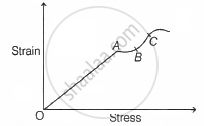
The stress-strain graph of a material is shown in the figure. The region in which the material is elastic is ______.