Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
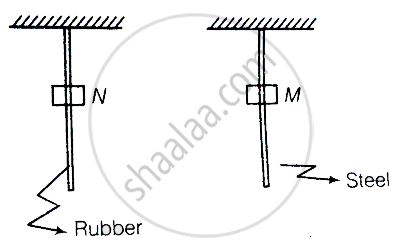
Consider two cylindrical rods of identical dimensions, one of rubber and the other of steel. Both the rods are fixed rigidly at one end to the roof. A mass M is attached to each of the free ends at the centre of the rods.
पर्याय
Both the rods will elongate but there shall be no perceptible change in shape.
The steel rod will elongate and change shape but the rubber rod will only elongate.
The steel rod will elongate without any perceptible change in shape, but the rubber rod will elongate and the shape of the bottom edge will change to an ellipse.
The steel rod will elongate, without any perceptible change in shape, but the rubber rod will elongate with the shape of the bottom edge tapered to a tip at the centre.
उत्तर
The steel rod will elongate, without any perceptible change in shape, but the rubber rod will elongate with the shape of the bottom edge tapered to a tip at the centre.
Explanation:
Consider the diagram. A mass M is attached at the centre. As the mass is connected to both the rods, both rod will be elongated, but due to different elastic properties of the material rubber changes shape.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Determine the volume contraction of a solid copper cube, 10 cm on an edge, when subjected to a hydraulic pressure of 7.0 ×106 Pa.
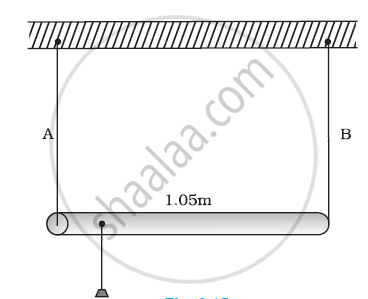
A rod of length 1.05 m having negligible mass is supported at its ends by two wires of steel (wire A) and aluminium (wire B) of equal lengths as shown in Figure. The cross-sectional areas of wires A and B are 1.0 mm2 and 2.0 mm2, respectively. At what point along the rod should a mass m be suspended in order to produce (a) equal stresses and (b) equal strains in both steel and aluminium wires.
A mild steel wire of length 1.0 m and cross-sectional area 0.50 × 10–2 cm2 is stretched, well within its elastic limit, horizontally between two pillars. A mass of 100 g is suspended from the mid-point of the wire. Calculate the depression at the midpoint.
Two strips of metal are riveted together at their ends by four rivets, each of diameter 6.0 mm. What is the maximum tension that can be exerted by the riveted strip if the shearing stress on the rivet is not to exceed 6.9 × 107 Pa? Assume that each rivet is to carry one-quarter of the load.
A rope 1 cm in diameter breaks if the tension in it exceeds 500 N. The maximum tension that may be given to a similar rope of diameter 2 cm is
A load of 10 kg is suspended by a metal wire 3 m long and having a cross-sectional area 4 mm2. Find (a) the stress (b) the strain and (c) the elongation. Young modulus of the metal is 2.0 × 1011 N m−2.
The maximum load a wire can withstand without breaking, when its length is reduced to half of its original length, will ______.
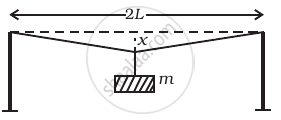
A mild steel wire of length 2L and cross-sectional area A is stretched, well within elastic limit, horizontally between two pillars (Figure). A mass m is suspended from the mid point of the wire. Strain in the wire is ______.
The area of the cross-section of the rope used to lift a load by a crane is 2.5 × 10-4m2. The maximum lifting capacity of the crane is 10 metric tons. To increase the lifting capacity of the crane to 25 metric tons, the required area of cross-section of the rope should be ______.
(take g = 10 ms-2)
Answer in one sentence:
What is an elastomer?
