Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A transverse wave travels along the Z-axis. The particles of the medium must move
पर्याय
along the Z-axis
along the X-axis
along the Y-axis
in the X-Y plane.
उत्तर
in the X–Y plane
In a transverse wave, particles move perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. In other words, if a wave moves along the Z-axis, the particles will move in the X–Y plane.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A wire of density ‘ρ’ and Young’s modulus ‘Y’ is stretched between two rigid supports separated by a distance ‘L’ under tension ‘T’. Derive an expression for its frequency in fundamental mode. Hence show that `n=1/(2L)sqrt((Yl)/(rhoL))` where symbols have their usual meanings
Explain why (or how): Bats can ascertain distances, directions, nature, and sizes of the obstacles without any “eyes”,
Explain why (or how) The shape of a pulse gets distorted during propagation in a dispersive medium.
You are walking along a seashore and a mild wind is blowing. Is the motion of air a wave motion?
A mechanical wave propagates in a medium along the X-axis. The particles of the medium
(a) must move on the X-axis
(b) must move on the Y-axis
(c) may move on the X-axis
(d) may move on the Y-axis.
A wave going in a solid
(a) must be longitudinal
(b) may be longitudinal
(c) must be transverse
(d) may be transverse.
A wave moving in a gas
A particle on a stretched string supporting a travelling wave, takes 5⋅0 ms to move from its mean position to the extreme position. The distance between two consecutive particles, which are at their mean positions, is 2⋅0 cm. Find the frequency, the wavelength and the wave speed.
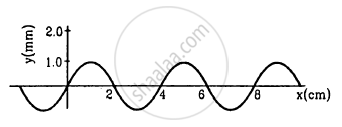
Figure shows a plot of the transverse displacements of the particles of a string at t = 0 through which a travelling wave is passing in the positive x-direction. The wave speed is 20 cm s−1. Find (a) the amplitude, (b) the wavelength, (c) the wave number and (d) the frequency of the wave.
A steel wire of length 64 cm weighs 5 g. If it is stretched by a force of 8 N, what would be the speed of a transverse wave passing on it?
A vertical rod is hit at one end. What kind of wave propagates in the rod if (a) the hit is made vertically (b) the hit is made horizontally?
Consider the following statements about sound passing through a gas.
(A) The pressure of the gas at a point oscillates in time.
(B) The position of a small layer of the gas oscillates in time.
A transverse wave described by \[y = \left( 0 \cdot 02 m \right) \sin \left( 1 \cdot 0 m^{- 1} \right) x + \left( 30 s^{- 1} \right)t\] propagates on a stretched string having a linear mass density of \[1 \cdot 2 \times {10}^{- 4} kg m^{- 1}\] the tension in the string.
A tuning fork of frequency 440 Hz is attached to a long string of linear mass density 0⋅01 kg m−1 kept under a tension of 49 N. The fork produces transverse waves of amplitude 0⋅50 mm on the string. (a) Find the wave speed and the wavelength of the waves. (b) Find the maximum speed and acceleration of a particle of the string. (c) At what average rate is the tuning fork transmitting energy to the string?
If the speed of a transverse wave on a stretched string of length 1 m is 60 m−1, what is the fundamental frequency of vibration?
Three resonant frequencies of a string are 90, 150 and 210 Hz. (a) Find the highest possible fundamental frequency of vibration of this string. (b) Which harmonics of the fundamental are the given frequencies? (c) Which overtones are these frequencies? (d) If the length of the string is 80 cm, what would be the speed of a transverse wave on this string?
The phenomenon of beats can take place
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = 2 cos (3x) sin (10t)
