Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain why (or how): Bats can ascertain distances, directions, nature, and sizes of the obstacles without any “eyes”,
उत्तर १
Bats emit very high-frequency ultrasonic sound waves. These waves get reflected back toward them by obstacles. A bat receives a reflected wave (frequency) and estimates the distance, direction, nature, and size of an obstacle with the help of its brain senses.
उत्तर २
Bats emit ultrasonic waves of high frequency from their mouths. These waves after being reflected back from the obstacles on their path are observed by the bats. These waves give them an idea of distance, direction, nature and size of the obstacles.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When longitudinal wave is incident at the boundary of denser medium, then............................
- compression reflects as a compression.
- compression reflects as a rarefaction.
- rarefaction reflects as a compression.
- longitudinal wave reflects as transverse wave.
Explain why (or how) Solids can support both longitudinal and transverse waves, but only longitudinal waves can propagate in gases
Explain why (or how) The shape of a pulse gets distorted during propagation in a dispersive medium.
A transverse wave travels along the Z-axis. The particles of the medium must move
Longitudinal waves cannot
Mark out the correct options.
Two wires of different densities but same area of cross section are soldered together at one end and are stretched to a tension T. The velocity of a transverse wave in the first wire is double of that in the second wire. Find the ratio of the density of the first wire to that of the second wire.
Consider the following statements about sound passing through a gas.
(A) The pressure of the gas at a point oscillates in time.
(B) The position of a small layer of the gas oscillates in time.
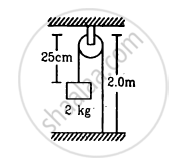
In the arrangement shown in figure , the string has a mass of 4⋅5 g. How much time will it take for a transverse disturbance produced at the floor to reach the pulley? Take g = 10 m s−2.
A circular loop of string rotates about its axis on a frictionless horizontal place at a uniform rate so that the tangential speed of any particle of the string is ν. If a small transverse disturbance is produced at a point of the loop, with what speed (relative to the string) will this disturbance travel on the string?
