Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Mark out the correct options.
पर्याय
The energy of any small part of a string remains constant in a travelling wave.
The energy of any small part of a string remains constant in a standing wave.
The energies of all the small parts of equal length are equal in a travelling wave.
The energies of all the small parts of equal length are equal in a standing wave.
उत्तर
The energy of any small part of a string remains constant in a standing wave.
A standing wave is formed when the energy of any small part of a string remains constant. If it does not, then there is transfer of energy. In that case, the wave is not stationary.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When longitudinal wave is incident at the boundary of denser medium, then............................
- compression reflects as a compression.
- compression reflects as a rarefaction.
- rarefaction reflects as a compression.
- longitudinal wave reflects as transverse wave.
When a transverse wave on a string is reflected from the free end, the phase change produced is ..............
(a) zero rad
(b) ` pi/2 ` rad
(c) `(3pi)/4` rad
(d) `pi` rad
A wire of density ‘ρ’ and Young’s modulus ‘Y’ is stretched between two rigid supports separated by a distance ‘L’ under tension ‘T’. Derive an expression for its frequency in fundamental mode. Hence show that `n=1/(2L)sqrt((Yl)/(rhoL))` where symbols have their usual meanings
A transverse harmonic wave on a string is described by y(x, t) = 3.0 sin (36 t + 0.018 x + π/4)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. The positive direction of x is from left to right.
(a) Is this a travelling wave or a stationary wave?
If it is travelling, what are the speed and direction of its propagation?
(b) What are its amplitude and frequency?
(c) What is the initial phase at the origin?
(d) What is the least distance between two successive crests in the wave?
Explain why (or how): Bats can ascertain distances, directions, nature, and sizes of the obstacles without any “eyes”,
A mechanical wave propagates in a medium along the X-axis. The particles of the medium
(a) must move on the X-axis
(b) must move on the Y-axis
(c) may move on the X-axis
(d) may move on the Y-axis.
A transverse wave travels along the Z-axis. The particles of the medium must move
A wave moving in a gas
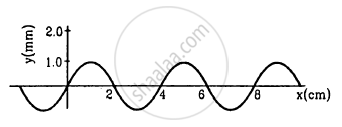
Figure shows a plot of the transverse displacements of the particles of a string at t = 0 through which a travelling wave is passing in the positive x-direction. The wave speed is 20 cm s−1. Find (a) the amplitude, (b) the wavelength, (c) the wave number and (d) the frequency of the wave.
A steel wire of length 64 cm weighs 5 g. If it is stretched by a force of 8 N, what would be the speed of a transverse wave passing on it?
A circular loop of string rotates about its axis on a frictionless horizontal place at a uniform rate so that the tangential speed of any particle of the string is ν. If a small transverse disturbance is produced at a point of the loop, with what speed (relative to the string) will this disturbance travel on the string?
A transverse wave of amplitude 0⋅50 mm and frequency 100 Hz is produced on a wire stretched to a tension of 100 N. If the wave speed is 100 m s−1, what average power is the source transmitting to the wire?
If the speed of a transverse wave on a stretched string of length 1 m is 60 m−1, what is the fundamental frequency of vibration?
A wire, fixed at both ends is seen to vibrate at a resonant frequency of 240 Hz and also at 320 Hz. (a) What could be the maximum value of the fundamental frequency? (b) If transverse waves can travel on this string at a speed of 40 m s−1, what is its length?
The phenomenon of beats can take place
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = 2 cos (3x) sin (10t)
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
`"y" = 2sqrt(x - "vt")`
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = 3 sin (5x – 0.5t) + 4 cos (5x – 0.5t)
