Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A Young's double slit experiment is performed with white light.
(a) The central fringe will be white.
(b) There will not be a completely dark fringe.
(c) The fringe next to the central will be red.
(d) The fringe next to the central will be violet.
उत्तर
(a) The central fringe will be white.
(b) There will not be a completely dark fringe.
(d) The fringe next to the central will be violet.
The superposition of all the colours at the central maxima gives the central band a white colour. As we go from the centre to corner, the fringe colour goes from violet to red. There will not be a completely dark fringe, as complete destructive interference does not take place.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the fringe pattern on the screen is actually a superposition of slit diffraction from each slit.
In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the slits are separated by 0.28 mm and the screen is placed 1.4 m away. The distance between the central bright fringe and the fourth bright fringe is measured to be 1.2 cm. Determine the wavelength of light used in the experiment.
Find the intensity at a point on a screen in Young's double slit experiment where the interfering waves have a path difference of (i) λ/6, and (ii) λ/2.
A parallel beam of light of wavelength 500 nm falls on a narrow slit and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 1 m away. It is observed that the first minimum is a distance of 2.5 mm away from the centre. Find the width of the slit.
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 800 nm and 600 nm is used to obtain the interference fringes in a Young's double slit experiment on a screen placed 1 · 4 m away. If the two slits are separated by 0·28 mm, calculate the least distance from the central bright maximum where the bright fringes of the two wavelengths coincide.
Two polaroids ‘A’ and ‘B’ are kept in crossed position. How should a third polaroid ‘C’ be placed between them so that the intensity of polarized light transmitted by polaroid B reduces to 1/8th of the intensity of unpolarized light incident on A?
In Young’s double slit experiment to produce interference pattern, obtain the conditions for constructive and destructive interference. Hence deduce the expression for the fringe width.
How does the fringe width get affected, if the entire experimental apparatus of Young is immersed in water?
In Young’s experiment interference bands were produced on a screen placed at 150 cm from two slits, 0.15 mm apart and illuminated by the light of wavelength 6500 Å. Calculate the fringe width.
A thin transparent sheet is placed in front of a Young's double slit. The fringe-width will _____________ .
A Young's double slit apparatus has slits separated by 0⋅28 mm and a screen 48 cm away from the slits. The whole apparatus is immersed in water and the slits are illuminated by red light \[\left( \lambda = 700\text{ nm in vacuum} \right).\] Find the fringe-width of the pattern formed on the screen.
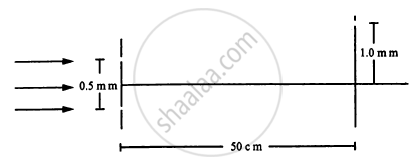
White coherent light (400 nm-700 nm) is sent through the slits of a Young's double slit experiment (see the following figure). The separation between the slits is 0⋅5 mm and the screen is 50 cm away from the slits. There is a hole in the screen at a point 1⋅0 mm away (along the width of the fringes) from the central line. (a) Which wavelength(s) will be absent in the light coming from the hole? (b) Which wavelength(s) will have a strong intensity?
In a Young's double slit experiment, \[\lambda = 500\text{ nm, d = 1.0 mm and D = 1.0 m.}\] Find the minimum distance from the central maximum for which the intensity is half of the maximum intensity.
The line-width of a bright fringe is sometimes defined as the separation between the points on the two sides of the central line where the intensity falls to half the maximum. Find the line-width of a bright fringe in a Young's double slit experiment in terms of \[\lambda,\] d and D where the symbols have their usual meanings.
In Young's double slit experiment the slits are 0.589 mm apart and the interference is observed on a screen placed at a distance of 100 cm from the slits. It is found that the 9th bright fringe is at a distance of 7.5 mm from the dark fringe which is second from the center of the fringe pattern. Find the wavelength of the light used.
An unpolarised beam of intensity 2a2 passes through a thin polaroid. Assuming zero absorption in the polaroid, the intensity of emergent plane polarised light will be
Monochromatic green light of wavelength 5 × 10-7 m illuminates a pair of slits 1 mm apart. The separation of bright lines in the interference pattern formed on a screen 2 m away is ______.
- Assertion (A): In Young's double slit experiment all fringes are of equal width.
- Reason (R): The fringe width depends upon the wavelength of light (λ) used, the distance of the screen from the plane of slits (D) and slits separation (d).
In Young's double-slit experiment, the screen is moved away from the plane of the slits. What will be its effect on the following?
- The angular separation of the fringes.
- Fringe-width.
