Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
ABCD is a parallelogram and E is the mid-point of BC. DE and AB when produced meet at F. Then, AF =
पर्याय
\[\frac{3}{2}AB\]
2 AB
3 AB
\[\frac{5}{4}AB\]
उत्तर
Parallelogram ABCD is given with E as the mid-point of BC.
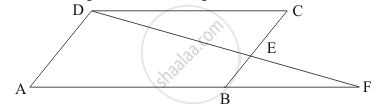
DE and AB when produced meet at F
We need to find AF.
Since ABCD is a parallelogram, then DC || AB
Therefore, DC || AF
Then, the alternate interior angles should be equal.
Thus, ∠DCE = ∠CBF …… (I)
In ΔDEC and ΔFEB:
∠DEC = ∠CBF (From(I))
CE = BE (E is the mid-point of BC)
∠CED = ∠BEF (Vertically opposite angles)
ΔDEC ≅ ΔFEB (by ASA Congruence property)
We know that the corresponding angles of congruent triangles should be equal.
Therefore,
DC = BF
But,
DC = AB (Opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal)
Therefore,
BF = AB …… (II)
Now,
AF = BF + AB
From (II),we get:
AF = AB +AB
AF = 2AB
Hence the correct choice is (b).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that if the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles, then it is a rhombus.
The following statement are true and false .
In any quadrilateral, if a pair of opposite sides is equal, it is a parallelogram.
The following statement are true and false .
If three angles of a quadrilateral are equal, it is a parallelogram .
If measures opposite angles of a parallelogram are (60 − x)° and (3x − 4)°, then find the measures of angles of the parallelogram.
In the given figure, ABCD and AEFG are two parallelograms. If ∠C = 58°, find ∠F.
PQRS is a quadrilateral, PR and QS intersect each other at O. In which of the following case, PQRS is a parallelogram?
PQ = 7 cm, QR = 7 cm, RS = 8 cm, SP = 8 cm
The figure formed by joining the mid-points of the adjacent sides of a quadrilateral is a
In a parallelogram ABCD, if ∠DAB = 75° and ∠DBC = 60°, then ∠BDC =
ABCD is a parallelogram and E and F are the centroids of triangles ABD and BCDrespectively, then EF =
The diagonals of a parallelogram ABCD intersect at O. If ∠BOC = 90° and ∠BDC = 50°, then ∠OAB =
