Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An isosceles triangle of vertical angle 2θ is inscribed in a circle of radius a. Show that the area of triangle is maximum when θ = `pi/6`
उत्तर
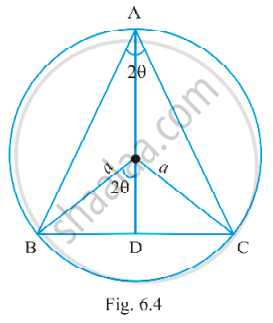
Let ABC be an isosceles triangle inscribed in the circle with radius a such that AB = AC.
AD = AO + OD = a + a cos2θ and BC = 2BD = 2a sin2θ (see fig. 16.4)
Therefore, area of the triangle ABC
i.e. ∆ = `1/2` BC . AD
= `1/2 2"a" sin2theta * ("a" + "a" cos2theta)`
= a2sin2θ (1 + cos2θ)
⇒ ∆ = `"a"^2sin2theta + 1/2 "a"^2 sin4theta`
Therefore, `("d"∆)/("d"theta)` = 2a2cos2θ + 2a2cos4θ
= 2a2(cos2θ + cos4θ)
`("d"∆)/("d"theta)` = cos2θ = –cos4θ = cos (π – 4θ)
Therefore, 2θ = π – 4θ
⇒ θ = `pi/6`
`("d"^2∆)/("d"theta)` = 2a2 (–2sin2θ – 4sin4θ) < 0 `("at" theta = pi/6)`.
Therefore, Area of triangle is maximum when θ = `pi/6`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that height of the cylinder of greatest volume which can be inscribed in a right circular cone of height h and semi vertical angle α is one-third that of the cone and the greatest volume of cylinder is `4/27 pih^3` tan2α.
\[f\left( x \right) = \begin{cases}- 4x + 5, & 0 \leq x \leq 1 \\ 2x - 3, & 1 < x \leq 2\end{cases}\] Discuss the applicability of Rolle's theorem for the following function on the indicated intervals ?
Verify Rolle's theorem for the following function on the indicated interval f(x) = x2 − 4x + 3 on [1, 3] ?
Verify Rolle's theorem for the following function on the indicated interval f (x) = x(x − 1)2 on [0, 1] ?
Verify Rolle's theorem for the following function on the indicated interval f (x) = x(x − 4)2 on the interval [0, 4] ?
Verify Rolle's theorem for the following function on the indicated interval f(x) = cos 2x on [0, π] ?
Verify Rolle's theorem for the following function on the indicated interval f(x) = sin x + cos x on [0, π/2] ?
Verify Rolle's theorem for the following function on the indicated interval f(x) = x2 − 5x + 4 on [1, 4] ?
At what point on the following curve, is the tangent parallel to x-axis y = \[e^{1 - x^2}\] on [−1, 1] ?
Examine if Rolle's theorem is applicable to any one of the following functions.
(i) f (x) = [x] for x ∈ [5, 9]
(ii) f (x) = [x] for x ∈ [−2, 2]
Can you say something about the converse of Rolle's Theorem from these functions?
Verify Lagrange's mean value theorem for the following function on the indicated intervals. find a point 'c' in the indicated interval as stated by the Lagrange's mean value theore f(x) = (x − 1)(x − 2)(x − 3) on [0, 4] ?
Verify Lagrange's mean value theorem for the following function on the indicated intervals. find a point 'c' in the indicated interval as stated by the Lagrange's mean value theore f(x) = tan−1 x on [0, 1] ?
Verify Lagrange's mean value theorem for the following function on the indicated intervals. find a point 'c' in the indicated interval as stated by the Lagrange's mean value theorem \[f\left( x \right) = \sqrt{x^2 - 4} \text { on }[2, 4]\] ?
Verify Lagrange's mean value theorem for the following function on the indicated intervals. find a point 'c' in the indicated interval as stated by the Lagrange's mean value theorem f(x) = sin x − sin 2x − x on [0, π] ?
State Lagrange's mean value theorem ?
If the value of c prescribed in Rolle's theorem for the function f (x) = 2x (x − 3)n on the interval \[[0, 2\sqrt{3}] \text { is } \frac{3}{4},\] write the value of n (a positive integer) ?
If 4a + 2b + c = 0, then the equation 3ax2 + 2bx + c = 0 has at least one real root lying in the interval
The value of c in Rolle's theorem when
f (x) = 2x3 − 5x2 − 4x + 3, x ∈ [1/3, 3] is
The value of c in Rolle's theorem for the function \[f\left( x \right) = \frac{x\left( x + 1 \right)}{e^x}\] defined on [−1, 0] is
Find the points on the curve x2 + y2 − 2x − 3 = 0 at which the tangents are parallel to the x-axis ?
Show that height of the cylinder of greatest volume which can be inscribed in a right circular cone of height h and semi-vertical angle α is one-third that of the cone and the greatest volume of the cylinder is `(4)/(27) pi"h"^3 tan^2 α`.
Show that the local maximum value of `x + 1/x` is less than local minimum value.
Find the difference between the greatest and least values of the function f(x) = sin2x – x, on `[- pi/2, pi/2]`
If f(x) = `1/(4x^2 + 2x + 1)`, then its maximum value is ______.
Prove that f(x) = sinx + `sqrt(3)` cosx has maximum value at x = `pi/6`
The least value of the function f(x) = `"a"x + "b"/x` (where a > 0, b > 0, x > 0) is ______.
If the graph of a differentiable function y = f (x) meets the lines y = – 1 and y = 1, then the graph ____________.
Let y = `f(x)` be the equation of a curve. Then the equation of tangent at (xo, yo) is :-
