Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An organic compound having the molecular formula C3H6O can exist in the form of two isomers A and B having different functional groups. The isomer A is a liquid which is used as a solvent for nail polish. The isomer B is also a liquid. An aqueous solution of one of the lower homologues of B is used for preserving biological specimens in the laboratory
(a) What is compound A?
(b) Write the electron-dot structure of A.
(c) What is compound B?
(d) Write the electron-dot structure of B.
(e) Name the lower homologue of compound B which is used in preserving biological specimens.
उत्तर
(a) The isomer A is propanone (acetone).
(b) The electron-dot structure of propanone is::
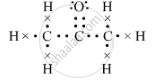
(c) The isomer B is propanal.
(d)The electron-dot structure of propanal is:
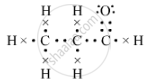
(e) Methanal or formaldehyde is the lower homologue of compound B, which is used to preserve biological specimens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of homologous series having general formula CnH2n + 2.
Give the structural formula for 1, 2-dichloroethane
Define a homologous series. Give the name and structural formula of one homologue of the following:
CH3OH
What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
The molecular formula of a homologue of butane is:
(a) C4H8
(b) C3H6
(c) C4H6
(d) C3H8
 .
.
Distinguish between homologous organs and analogous organs. In which category would you place wings of a bird and wings of a bat? Justify your answer giving a suitable reason.
Copy and complete the following table which relates to three homologus series of hydrocarbons:
| General formula | CnH2n | CnH2n-2 | CnH2n+2 |
| IUPAC name of the homologus series | |||
| Characteristic bond type | Single bonds | ||
| IUPAC name of the first member of the series | |||
| Type of reaction with chlorine | Addition |
The phenomenon in which compounds having different structural formulae have the same molecular formula is called _______.
A carbon compound ‘A’ having melting point 156K and boiling point 351K, with molecular formula C2H6O is soluble in water in all proportions.
- Identify ‘A’ and draw its electron dot structure.
- Give the molecular formulae of any two homologues of ‘A’.
