Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An organic compound having the molecular formula C3H6O can exist in the form of two isomers A and B having different functional groups. The isomer A is a liquid which is used as a solvent for nail polish. The isomer B is also a liquid. An aqueous solution of one of the lower homologues of B is used for preserving biological specimens in the laboratory
(a) What is compound A?
(b) Write the electron-dot structure of A.
(c) What is compound B?
(d) Write the electron-dot structure of B.
(e) Name the lower homologue of compound B which is used in preserving biological specimens.
Solution
(a) The isomer A is propanone (acetone).
(b) The electron-dot structure of propanone is::
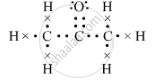
(c) The isomer B is propanal.
(d)The electron-dot structure of propanal is:
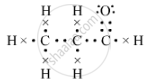
(e) Methanal or formaldehyde is the lower homologue of compound B, which is used to preserve biological specimens.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is meant by homologous series of carbon compounds?
Write the molecular formula of two consecutive members of homologous series of aldehydes. State which part of these compounds determines their
- physical and
- chemical properties
Define a homologous series. Give the name and structural formula of one homologue of the following:
CH3OH
Copy and complete the following table which relates to three homologus series of hydrocarbons:
| General formula | CnH2n | CnH2n-2 | CnH2n+2 |
| IUPAC name of the homologus series | |||
| Characteristic bond type | Single bonds | ||
| IUPAC name of the first member of the series | |||
| Type of reaction with chlorine | Addition |
Two statements are given - one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R).
Assertion (A): In a homologous series of alcohols, the formula for the second member is C2H5OH and the third member is C3H7OH.
Reason (R): The difference between the molecular masses of the two consecutive members of a homologous series is 144.
There are different general molecular formula for all members of the homologous series.
Complete the following table for homologous series of Alkenes.
| Name | Molecular formula | Condensed structural formula | Number of carbon atom | Number of -CH2- units | Boiling point °C |
| Ethene | C2H4 | CH2 = CH2 | 2 | 0 | -102 |
| Propene | C3H6 | CH3–CH = CH2 | 3 | 1 | -48 |
| 1-Butene | C4H8 | CH3–CH2–CH = CH2 | ______ | ______ | -6.5 |
| 1-Pentene | C5H10 | CH3–CH2–CH2–CH = CH2 | ______ | ______ | 30 |
Successive members of a homologous series vary by how many atomic mass unit?
Consider the carbon compounds having following molecular formula:
(i) C3H6 (ii) C3H8 (iii) C4H6 (iv) C6H6 (v) C6H12
- State the number of double covalent bonds present in C3H8.
- Write the formula of first member of the homologous series to which the carbon compound C4H6 belongs.
- Which one of the above compounds forms a ring structure of carbon atoms?
- Identify, which of the above compounds, is a member of alkane series.
