Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Angles of a quadrilateral are (4x)°, 5(x+2)°, (7x – 20)° and 6(x+3)°. Find :
(i) the value of x.
(ii) each angle of the quadrilateral.
उत्तर
Angles of quadrilateral are,
(4x)°, 5(x+2)°, (7x – 20)° and 6(x+3)°
∴ 4x + 5(x + 2) + (7x - 20) + 6(x + 3) = 360°
4x + 5x + 10 + 7x - 20 + 6x + 18 = 360°
22x + 8 = 360°
22x = 360° - 8°
22x = 352°
x = 16°
Hence angles are,
(4x)° = (4 × 16)° = 64°
5(x + 2)° = 5(16 + 2)° = 90°
(7x - 20)° = (7 × 16 - 20)° = 92°
6(x + 3)° = 6(16 + 3) = 114°
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the sum of the measures of the angels of a convex quadrilateral? Will this property hold if the quadrilateral is not convex? (Make a non-convex quadrilateral and try!)
Define the following term Convex Quadrilateral .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Sides.
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Angles .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Adjacent angles .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Opposite angles .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
A quadrilateral has .... diagonals.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
In a quadrilateral the point of intersection of the diagonals lies in .... of the quadrilateral.
The angles of a quadrilateral are 110°, 72°, 55° and x°. Find the value of x.
Two angles of a quadrilateral are of measure 65° and the other two angles are equal. What is the measure of each of these two angles?
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is three times the sum of its exterior angles. Determine the number of sided of the polygon.
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 89° and 113°. If the other two angles are equal; find the equal angles.
In quadrilateral ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A : ∠D = 1 : 2 and ∠C : ∠B = 4 : 5
(i) Calculate each angle of the quadrilateral.
(ii) Assign a special name to quadrilateral ABCD
Use the following figure to find the value of x
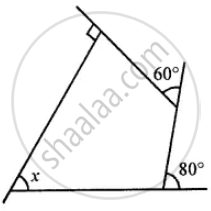
In a trapezium ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A = x° and ∠D = (3x – 20)°; find the value of x.
In an isosceles trapezium one pair of opposite sides are _____ to each Other and the other pair of opposite sides are _____ to each other.
Two diagonals of an isosceles trapezium are x cm and (3x – 8) cm. Find the value of x.
In a parallelogram ABCD, its diagonals AC and BD intersect each other at point O.
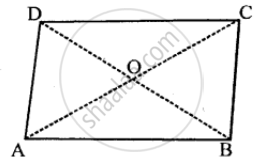
If AC = 12 cm and BD = 9 cm ; find; lengths of OA and OD.
The diagonals of a rhombus are 6 .cm and 8 cm. State the angle at which these diagonals intersect.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
Find the angles of a pentagon which are in the ratio 4: 4: 6: 7: 6.
One angle of a hexagon is 140° and the remaining angles are in the ratio 4 : 3 : 4 : 5 : 4. Calculate the measures of the smallest and the largest angles.
ΔPQR and ΔSQR are on the same base QR with P and S on opposite sides of line QR, such that area of ΔPQR is equal to the area of ΔSQR. Show that QR bisects PS.
D and E are the mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively of ∆ABC. DE is produced to F. To prove that CF is equal and parallel to DA, we need an additional information which is ______.
A quadrilateral can have all four angles as obtuse.
In the given figure.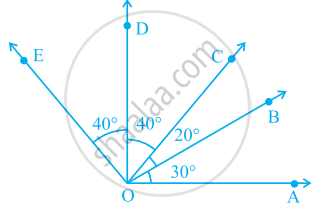
∠AOD is a/an ____ angle
The number of right angles in a straight angle is ______ and that in a complete angle is ______.
In given figure, name any two angles that appear to be obtuse angles.
