Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In quadrilateral ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A : ∠D = 1 : 2 and ∠C : ∠B = 4 : 5
(i) Calculate each angle of the quadrilateral.
(ii) Assign a special name to quadrilateral ABCD
उत्तर
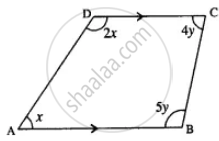
(i) ∵ ∠A : ∠D = 1 : 2
Let ∠A = x and ∠D = 2x
∵ ∠C : ∠B = 4 : 5
Let ∠C = 4y and ∠B = 5y
∵ AB || DC
∴ ∠A + ∠D = 180°
x + 2x = 180°
3x = 180°
x = 60°
∴ A = 60°
∠D = 2x = 2 × 60 = 120°
Again ∠B + ∠C = 180°
5y + 4y = 180°
9y = 180°
y = 20°
∴ ∠B = 5y = 5 x 20 = 100°
∠C = 4y = 4 x 20 = 80°
Hence ∠A = 60°; ∠B = 100°; ∠C = 80°
and ∠D = 120°
(ii) `square` ABCD is a trapezium.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Adjacent sides .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Opposite angles .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
The sum of the angles of a quiadrilateral is .... right angles.
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
In a quadrilateral the point of intersection of the diagonals lies in .... of the quadrilateral.
In Fig. 16.19, ABCD is a quadrilateral.
Name a pair of adjacent sides.
The sides of a quadrilateral are produced in order. What is the sum of the four exterior angles?
In a quadrilateral ABCD, CO and DO are the bisectors of ∠C and ∠D respectively. Prove that \[∠COD = \frac{1}{2}(∠A + ∠B) .\]
The measure of angles of a hexagon are x°, (x − 5)°, (x − 5)°, (2x − 5)°, (2x − 5)°, (2x + 20)°. Find the value of x.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
If both pairs of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are equal, then it is necessarily a ...............
Which of the following quadrilateral is not a rhombus?
Two angles of a quadrilateral are 68° and 76°. If the other two angles are in the ratio 5 : 7; find the measure of each of them.
Angles of a quadrilateral are (4x)°, 5(x+2)°, (7x – 20)° and 6(x+3)°. Find :
(i) the value of x.
(ii) each angle of the quadrilateral.
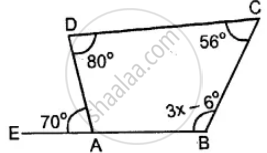
Use the information given in the following figure to find :
(i) x
(ii) ∠B and ∠C
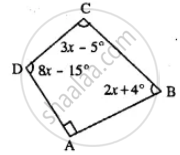
In quadrilateral PQRS, ∠P : ∠Q : ∠R : ∠S = 3 : 4 : 6 : 7.
Calculate each angle of the quadrilateral and then prove that PQ and SR are parallel to each other
(i) Is PS also parallel to QR?
(ii) Assign a special name to quadrilateral PQRS.
Use the information given in the following figure to find the value of x.
In a trapezium ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A = 78° and ∠C = 120. find angles B and D.
Angle A of an isosceles trapezium ABCD is 115°; find the angles B, C and D.
If three angles of a quadrilateral are 90° each, show that the given quadrilateral is a rectangle.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.
If angles A, B, C and D of the quadrilateral ABCD, taken in order, are in the ratio 3 : 7 : 6 : 4, then ABCD is a ______.
ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AB || DC and AD = BC. Prove that ∠A = ∠B and ∠C = ∠D.
In quadrilateral HOPE, the pairs of opposite sides are ______.
In quadrilateral ROPE, the pairs of adjacent angles are ______.
If a bicycle wheel has 48 spokes, then the angle between a pair of two consecutive spokes is ______.
In the given figure.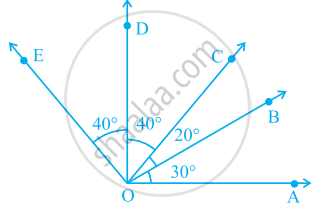
∠COA is a/an ______ angle
In the given figure.
∠AOE is a/an ______ angle
Number of angles less than 180° in figure is ______ and their names are ______.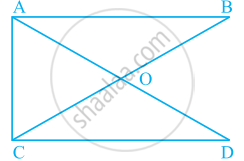
The number of straight angles in figure is ______.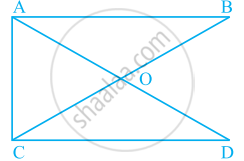
In given figure, What is BD – BE?
What conclusion can be drawn from part of given figure, if BD bisects ∠ABC?
