Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
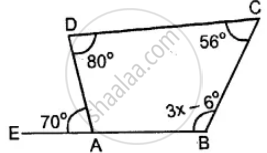
Use the information given in the following figure to find the value of x.
उत्तर
Take A, B, C, D as the vertices of Quadrilateral and BA is produced to E (say).
Since ∠EAD = 70°
∴ ∠DAB = 180° – 70°= 110° [EAB is a straight line and AD stands on it ∠EAD+ ∠DAB = 180°]
∴ 110° + 80° + 56° + 3x – 6° = 360°
[∵ sum of interior angles of a quadrilateral = 360°]
∴ 3x = 360° – 110° – 80° – 56° + 6°
3x = 360° – 240° = 120°
∴ x = 40°
संबंधित प्रश्न
The perimeter of a parallelogram is 22 cm . If the longer side measures 6.5 cm what is the measure of the shorter side?
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Angles .
In a quadrilateral, define of the following Opposite sides .
Complete of the following, so as to make a true statement:
In a quadrilateral the point of intersection of the diagonals lies in .... of the quadrilateral.
The angles of a quadrilateral are 110°, 72°, 55° and x°. Find the value of x.
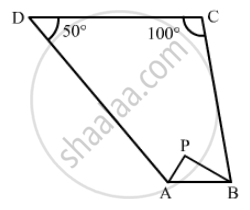
In Fig. 16.21, the bisectors of ∠A and ∠B meet at a point P. If ∠C = 100° and ∠D = 50°, find the measure of ∠APB.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, CO and DO are the bisectors of ∠C and ∠D respectively. Prove that \[∠COD = \frac{1}{2}(∠A + ∠B) .\]
PQRSTU is a regular hexagon. Determine each angle of ΔPQT.
Complete the following statement by means of one of those given in brackets against each:
f consecutive sides of a parallelogram are equal, then it is necessarily a ..................
Angles of a quadrilateral are (4x)°, 5(x+2)°, (7x – 20)° and 6(x+3)°. Find :
(i) the value of x.
(ii) each angle of the quadrilateral.
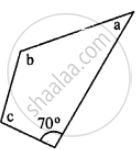
In the given figure : ∠b = 2a + 15 and ∠c = 3a + 5; find the values of b and c.
In a trapezium ABCD, side AB is parallel to side DC. If ∠A = x° and ∠D = (3x – 20)°; find the value of x.
Two diagonals of an isosceles trapezium are x cm and (3x – 8) cm. Find the value of x.
Two opposite angles of a parallelogram are 100° each. Find each of the other two opposite angles.
Observe the figure below and find out their name.

Observe the figure below and find out their name.
In a pentagon ABCDE, AB || ED and ∠B = 140°, ∠C = 2x° and ∠D = 3x°. Find ∠C and ∠D
If bisectors of ∠A and ∠B of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at P, of ∠B and ∠C at Q, of ∠C and ∠D at R and of ∠D and ∠A at S, then PQRS is a ______.
D and E are the mid-points of the sides AB and AC respectively of ∆ABC. DE is produced to F. To prove that CF is equal and parallel to DA, we need an additional information which is ______.
Measures of the two angles between hour and minute hands of a clock at 9 O’ clock are ______.
If a bicycle wheel has 48 spokes, then the angle between a pair of two consecutive spokes is ______.
The number of obtuse angles in figure is ______.
If the sum of two angles is greater than 180°, then which of the following is not possible for the two angles?
The number of straight angles in figure is ______.
The number of common points in the two angles marked in figure is ______.
In given figure, What is BD – BE?
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
BA ⊥BD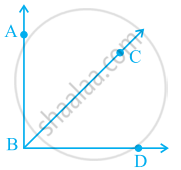
Using the information given, name the right angles in part of figure:
RT ⊥ ST